FIG.1.
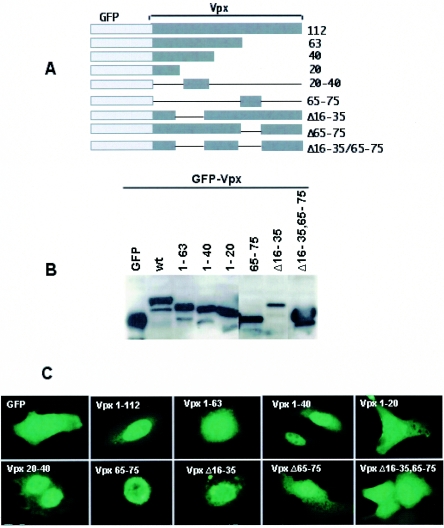
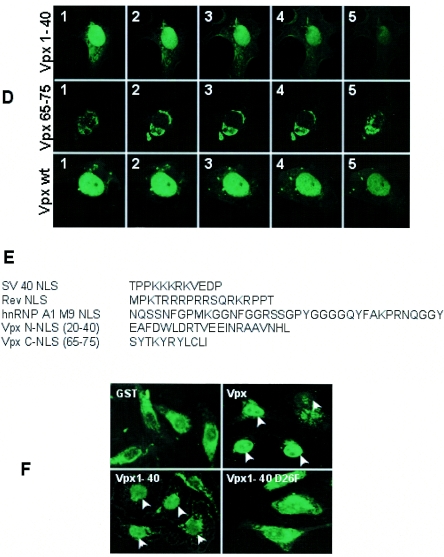
Evidence for the presence of two functional noncanonical NLSs in SIV Vpx. (A) Schematic diagram of GFP-Vpx fusion proteins. (B) Cos-7 cells were transfected with various GFP-Vpx deletion constructs, and cell lysates were prepared 16 h after transfection and resolved by SDS-12% PAGE. Western blot analysis was performed using monoclonal anti-GFP antibody at a 1:1,000 dilution followed by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated specific secondary antibodies (1:2,000 dilution) and developed using the Enhanced Chemiluminescence Plus detection system (Amersham Pharmacia). (C) Subcellular localization of GFP-Vpx fusion proteins. Vero cells were infected with vaccinia TF7-3 and transfected with various GFP-Vpx expression plasmids, and the localization of GFP fusion proteins was visualized directly after fixing of the transfected cells with 3% paraformaldehyde. Immunofluorescence analysis of these constructs suggests that GFP-Vpx1-40 and -Vpx20-40 translocate into the nucleus like full-length Vpx, which provides evidence for the presence of additional nuclear targeting signal in the amino terminus of Vpx. (D) Serial laser sections through a representative cell that expressed wild-type Vpx protein. N-terminal (Vpx1-40) and C-terminal (Vpx65-75) NLSs were obtained by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Photomicrographs were numbered from 1, which corresponds to the nuclear periphery, through 5, which corresponds to the region through which the cell was adsorbed to the slide. (E) Sequence comparison of various types of NLSs, such as the classical lysine-rich type (SV40 Tag NLS), the arginine-rich HIV-1 Rev NLS, and the M9 signal of hnRNP-A1 with Vpx nuclear targeting signals. Comparative analysis suggests that Vpx NLSs are distinct from previously known NLSs. (F) Sequence-specific nuclear import of Vpx in digitonin-permeabilized HeLa cells. In vitro nuclear import assays (2) were performed using fusions of wild-type Vpx (His tag-Vpx) and its amino-terminal NLS (aa 1 to 40) and a mutant variant of Vpx1-40 (Vpx1-40 D26F) to the carboxy terminus of GST as substrates. Rabbit reticulocyte lysate (Promega) containing an energy-regenerating system (1 mM ATP, 0.5 mM GTP, 10 mM creatine phosphate, and 0.4 μm creatine phosphokinase) was used as a source of cytosolic factors. Transport reactions were performed using His-Vpx, GST-Vpx1-40, and Vpx1-40 D26F fusion proteins at a concentration of 1 to 5 μg, while GST was used as a negative control. Transport reaction mixtures were set up in ice and then allowed to proceed for 60 min at 30°C. Samples were analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence using anti-Vpx or anti-GST antibody followed by Alexa fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody and epifluorescence. wt, wild type.