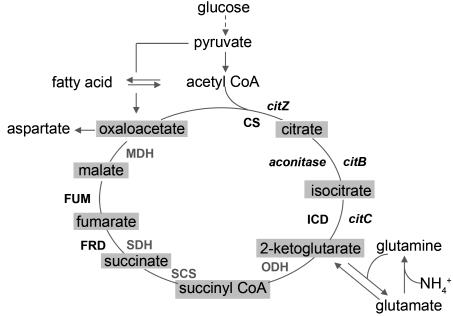
FIG. 1.
The Krebs citric acid cycle and its place in central metabolism. In L. monocytogenes, the Krebs cycle is incomplete because of the absence of ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, succinyl CoA synthetase, and succinic dehydrogenase. As a result, the enzymes form two independent half-cycles. The right half, corresponding to the tricarboxylic acid branch, synthesizes 2-ketoglutarate from acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate. 2-Ketoglutarate links central pathways of carbon catabolism and nitrogen assimilation. The left half operates counterclockwise and is used for respiration coupled to fumarate reduction. The source of malate is unknown (see the text). Enzymes are indicated by their names or abbreviations, and genes that encode the enzymes are indicated in italics. Missing enzymes are indicated in light typeface. Abbreviations: CS, citrate synthase; ICD, isocitrate dehydrogenase; ODH, ketoglutarate (oxoglutarate) dehydrogenase; SCS, succinyl CoA synthetase; SDH, succinic dehydrogenase; FRD, fumarate reductase; FUM, fumarate hydratase; MDH, malate dehydrogenase.