FIG. 6.
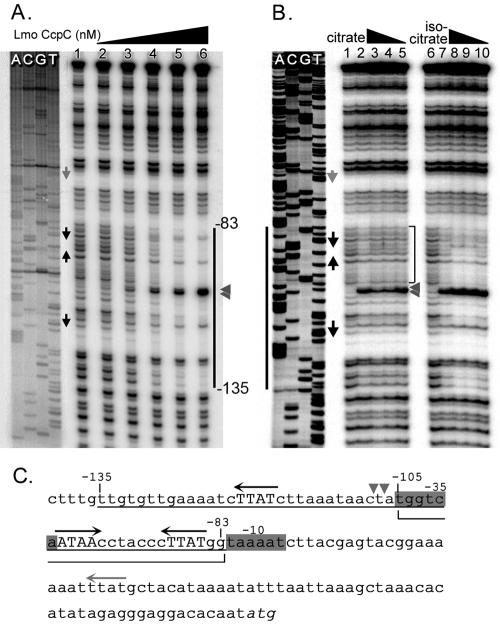
DNase I footprinting assay of interaction between CcpCLm-His6 and lmo0847. A. A 32P-labeled DNA fragment corresponding to the putative lmo0847 promoter region was incubated with different amounts of CcpCLm-His6 prior to DNase I digestion. Protein concentrations were as follows: 0 (lane 1), 3.9 (lane 2), 15.6 (lane 3), 62.5 (lane 4), 250 (lane 5), and 1,000 nM (lane 6). Sequence ladders obtained by Sanger sequencing of the same DNA fragment are shown to the left. Arrows show the elements of the putative CcpC binding site identified by genome search, and the vertical line indicates a region protected by CcpCLm-His6 from DNase I digestion. The gray arrowheads show sites of hypersensitivity to DNase I digestion in the presence of CcpCLm. B. Effect of citrate on the interaction of CcpCLm-His6 with lmo0847. The same DNA probe as in part A was incubated with CcpCLm-His6 (0 nM, lanes 1 and 6; 62.5 nM, lanes 2 to 5 and 7 to 10) in the presence of citrate (0.5%, lane 3; 0.25%, lane 4; 0.13%, lane 5) or isocitrate (0.5%, lane 8; 0.25%, lane 9; 0.13%, lane 10). The bracket indicates a region where protection by CcpCLm-His6 was inhibited specifically by citrate. The gray arrowheads indicate a site of hypersensitivity to DNase I that was abrogated in the presence of citrate. C. Sequence of the lmo0847 promoter region. The region protected by CcpCLm-His6 from DNase I digestion (positions −135 to −83) is underlined, and the region where CcpCLm-His6 was released by citrate (positions −105 to −83) is indicated by a bracket. The −35 and −10 regions of the putative promoter are shaded in gray, and the translational start codon is in italics.