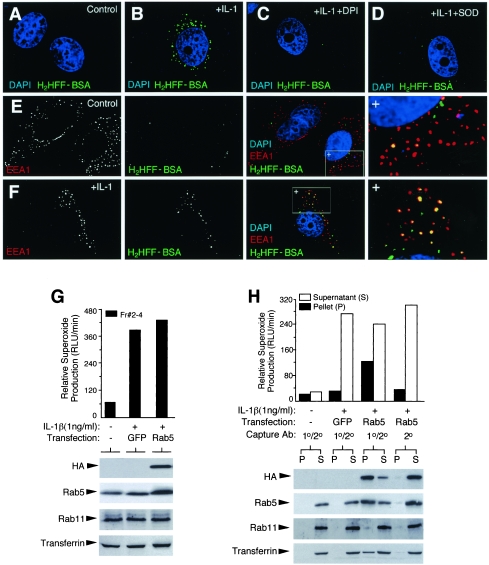
FIG. 4.
IL-1β induces ·O2− production by the early endosome compartment. (A to D) Endosomal ·O2− production in MCF-7 cells was visualized by H2HFF-BSA endosomal loading following a 10-min IL-1β (1.0 ng/ml) stimulation. Treatment conditions are indicated in the upper-right corner of each panel. H2HFF-BSA, IL-1β, DPI, and/or SOD was added at the time of IL-1β stimulation. Control cells were treated with vehicle (PBS). DAPI was included in the mounting medium for localization of the nucleus. Green staining denotes ·O2− production as fluorescent H2HFF. (E and F) Localization of EEA1 in MCF-7 cells treated with PBS (E) or IL-1β (F) in the presence of H2HFF-BSA for 10 min, followed by fixation. Anti-EEA1 was detected using a Texas Red secondary antibody, and slides were mounted in DAPI-containing medium. Black-and-white photomicrographs for each row depict the indicated EEA1 or H2HFF-BSA fluorescent channels. Combined three-color images are given, with the right-most panel being an enlargement of the boxed region marked with a +. Three types of vesicles are seen: red, EEA1 positive; yellow, EEA1 positive ·O2− producing; green, ·O2− producing non-EEA1 reactive. (G) MCF-7 cells were transfected with HA-Rab5 or GFP expression plasmids 48 h prior to IL-1β and biotin-transferrin treatment for 20 min. Vesicular peak fractions (Fr #2 to 4) were evaluated for NADPH oxidase activity and Western blotting for HA, Rab5, Rab11, or avidin-horseradish peroxidase. (H) Immuno-affinity isolation of HA-Rab5-associated endosomes using half of the vesicular peak fractions (2 to 4) shown in panel G. Dynabeads used for immuno-affinity isolation were coated with primary anti-HA antibody and/or secondary antibody, as indicated. Both the pellets (P) and supernatants (S) were evaluated for NADPH oxidase activity and Western blotted following immuno-affinity isolation, as for panel G. Equal percentages of the original sample were evaluated in panels G and H.