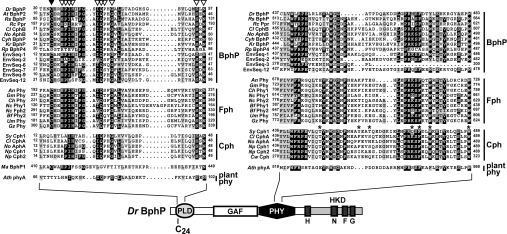
Figure 4. Amino acid sequence alignment of portions of PLD (left) and PHY (right) from members of the BphP, Fph, Cph and plant phy clades.
Alignments of the entire domains can be found in Supplemental Figures 2 and 3 (http://www.BiochemJ.org/bj/392/bj3920103add.htm). The sequences were grouped by their proposed inclusion into BphP, Fph, Cph and plant phy families. The position of each domain in the linear Phy sequence of D. radiodurans BphP is shown. Black and grey boxes denote identical and similar residues respectively. The numbers identify the amino acid positions for each sequence. The cysteine in the PLD important for bilin binding is identified by the closed arrowhead (Cys-24 in DrBphP). The open arrowheads identify conserved residues in AtBphP2 that were tested for their importance in BV IXα ligation (see Figure 7). The asterisks locate amino acids in the PHY domain identified as being important for the spectral properties of Synechocystis Cph1 [36]. Species and sequence designations can be found in the legend of Figure 3.