Figure 4.
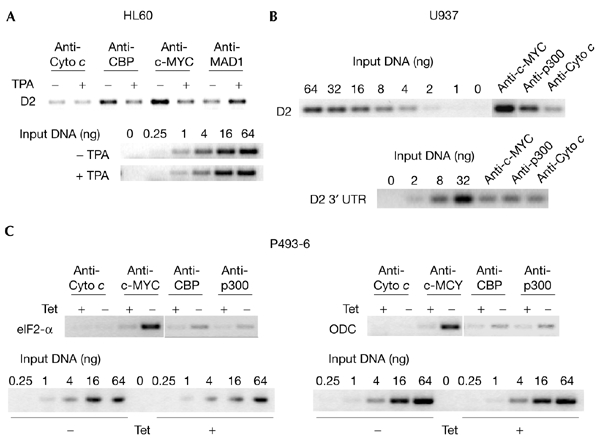
CBP and p300 are recruited to MYC target genes. (A) HL60 cells were grown exponentially (−) or induced to differentiate with 12-O-tetra-decanoyl-phorbol 13-acetate (TPA) (+) for 12 h. Chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed with antibodies recognizing the indicated proteins (c-MYC, N262; MAD1, C20; CBP, A22; Cyto c, SC7159). For PCR reactions, primers that amplify the region of the cyclin D2 promoter that contains the MYC/MAX binding site were used. For comparison, serial dilutions of input chromatin DNA were analysed. (B) Chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed on lysates of exponentially growing U937 cells. Specific antibodies were used as indicated (c-MYC, N262; p300, C22; Cyto c, SC7159). PCR reactions were carried out as in (A). (C) P493-6 cells were released from a tetracycline (Tet) block (−) or were mock treated (+). Cells were then crosslinked and processed. Immunoprecipitations and PCR reactions were carried out as in (A) and (B). CBP, cAMP-response-element-binding protein; D2, cyclin D2; ODC, ornithine decarboxylase; UTR, untranslated region.
