Figure 1.
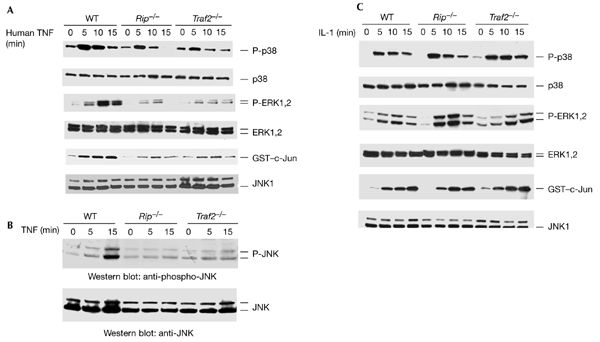
TNFR1-mediated p38, ERK and JNK activation require both TRAF2 and RIP. (A) Human-TNF-induced p38, ERK and JNK activation in wild-type, Rip−/− and Traf2−/− fibroblasts. Mouse fibroblasts were treated with human TNF (40 ng ml−1) for various durations or were left untreated as a control. Cell extracts were used for western blotting and in in vitro kinase assays to measure the activation of p38, ERK and JNK. (B) JNK activation in wild-type, Rip−/−, and Traf2−/− cells was measured using an anti-phospho-JNK antibody. (C) Interleukin-1 (IL-1)-induced p38, ERK and JNK activation. Wild-type, Rip−/− and Traf2−/− fibroblasts were either treated with IL-1 (4 ng ml−1) for various durations or were left untreated as a control. The activation of p38, ERK and JNK was measured as described in (A). These experiments were repeated three times. ERK, extracellular-signal-related kinase; GST, glutathione-S-transferase; hTNF, human TNF; JNK, c-Jun amino-terminal kinase; P-ERK, phospho-ERK; P-JNK, phospho-JNK; P-p38; phospho-p38; RIP, receptor-interacting protein; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; TNFR1, TNF receptor 1; TRAF2, TNFR-associated factor 2.
