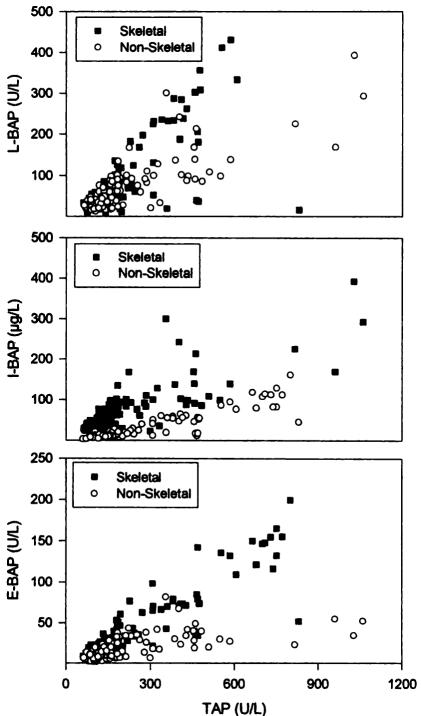
Figure 3.
Correlation between serum total and bone specific alkaline phosphatase. Patients with non-skeletal disease had chronic hepatic failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or chronic renal failure. Patients with skeletal disease had Paget’s disease of bone, primary or secondary hyperparathyroidism, or metastatic bone disease. TAP, total alkaline phosphatase; L-BAP, bone alkaline phosphatase measured by lectin precipitation assay; I-BAP, bone alkaline phosphatase measured by immunoradiometric assay (IRMA); E-BAP, bone alkaline phosphatase measured by enzyme linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) Reproduced from, Woitge H, Seibel MJ, Ziegler R. Comparison of total and bone-specific alkaline phosphatase in patients with nonskeletal disorders or metabolic bone disease Clin Chem 1996;42:1796–1804 with permission of the publisher of Clinical Chemistry.