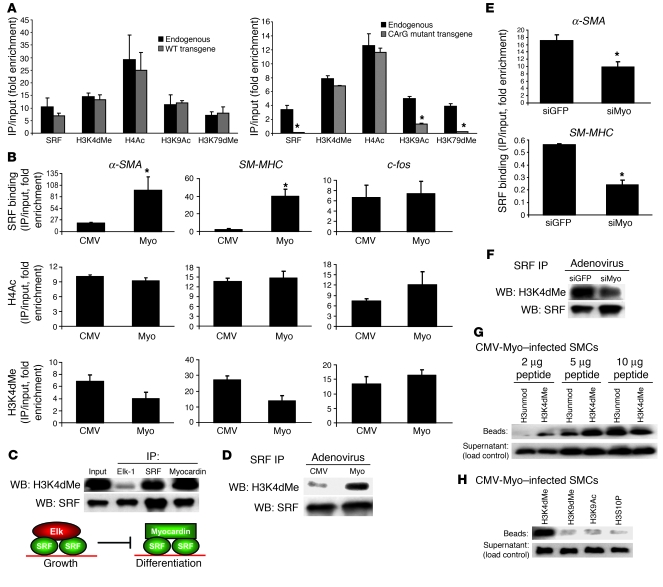
Figure 3. Identification modifications that contribute to myocardin/SRF binding to CArG boxes.
(A) α-SMA transgenes were stably transfected into rat aortic SMCs by the integrase system as described in Methods, and ChIP was performed with primers specific for the transgene and the endogenous gene. *P < 0.05 by Student’s t test. (B) SMCs were infected with adenovirus harboring CMV-myocardin (Myo) or CMV-empty (CMV) expression vectors, and ChIP was performed for SRF, H4Ac, and H3K4dMe. (C) SMCs were infected with adenovirus as in B. Elk-1, SRF, and FLAG-myocardin immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blotting for H3K4dMe and SRF. Nonimmune IgG antisera failed to immunoprecipitate SRF and H3K4dMe from SMC extracts in these and all other protein IP experiments (data not shown and Supplemental Figure 2). (D) SMCs were infected as in B, and SRF immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blotting for H3K4dMe and SRF. (E) SMCs were infected with adenoviruses expressing siRNAs to myocardin (siMyo) or GFP (siGFP; control). Chromatin was isolated, and ChIP measured levels of SRF binding to 5′-CArG boxes. (F) SMCs were infected as in E, and nuclear extracts were treated as in D. (G) Peptide binding assay with FLAG-myocardin as described in Methods. FLAG-myocardin immunoprecipitates collected from SMC extracts containing the corresponding biotinylated peptides were subjected to Western blotting using HRP-streptavidin. H3unmod, unmodified H3 peptide. (H) Myocardin peptide binding assay as in G, comparing the ability of myocardin to immunoprecipitate 2 μg of H3 peptides di-methylated at Lys4 (H3K4dMe), di-methylated at Lys9 (H3K9dMe), acetylated at Lys9, or phosphorylated at serine 10 (H3S10P).