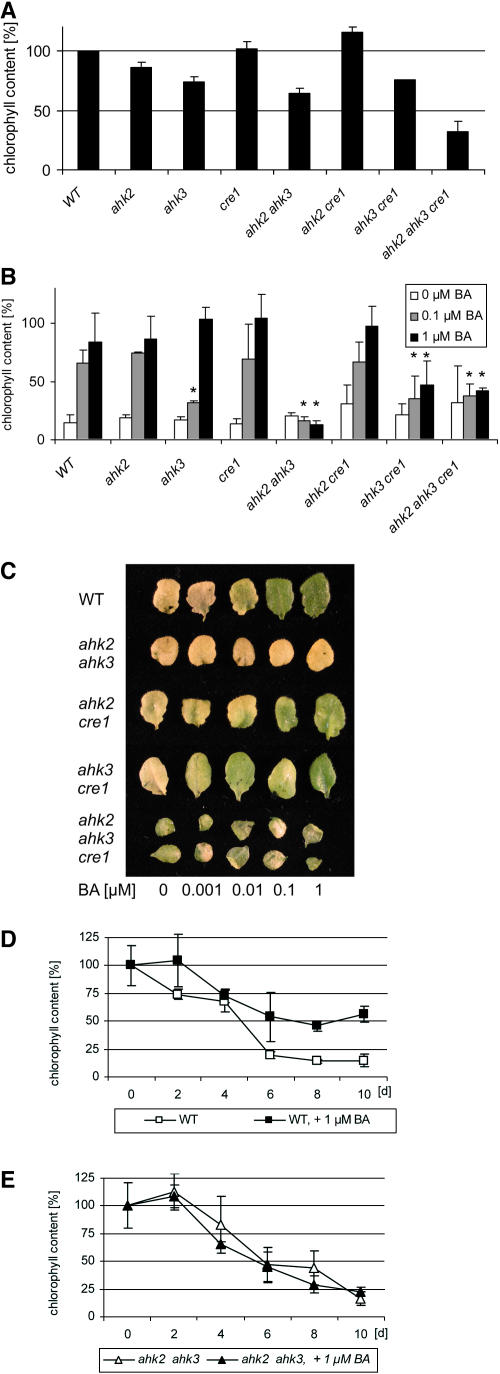
Figure 2.
AHK2 and AHK3 Are Required to Mediate Cytokinin-Dependent Chlorophyll Retention in the Dark.
(A) Chlorophyll content of in vitro–grown plants 24 DAG. Wild type (1.92 ± 0.01 μg/g leaf fresh weight) was set at 100%. For each of five independent samples per clone, five seventh leaves from different plants were pooled and analyzed. Error bars represent se (n = 5). The mutant alleles used were ahk2-5, ahk3-7, and cre1-2.
(B) Dark-induced senescence in a detached leaf assay and its inhibition by cytokinin. The leaf chlorophyll content before the start of dark incubation was set at 100% for each genotype tested. Bars: white, water plus DMSO; gray, 0.1 μM BA; black, 1 μM BA. Chlorophyll content at the beginning of the assay was for the wild type, 1.92 ± 0.01; ahk2-5, 1.64 ± 0.11; ahk3-7, 1.46 ± 0.11; cre1-2, 1.95 ± 0.14; ahk2-5 ahk3-7, 1.23 ± 0.03; ahk2-5 cre1-2, 2.23 ± 0.17; ahk3-7 cre1-2, 1.44 ± 0.09; ahk2-5 ahk3-7 cre1-2, 0.61 ± 0.31 μg/g leaf fresh weight. Asterisks represent significant changes to wild-type control at respective hormone concentrations. Error bars represent se (n = 5).
(C) Leaves of different genotypes at the end of the chlorophyll retention assay described in (B).
(D) Time course of dark-induced leaf senescence in wild-type leaves. The chlorophyll content at the beginning of the experiment was set at 100%. Three independent plates with five leaves per plate were examined at each time point and concentration. The graph shows pooled results from three independent experiments ±se (n = 3).
(E) Time course of dark-induced leaf senescence in leaves of the ahk2-5 ahk3-7 mutant. Conditions are as described in (D).