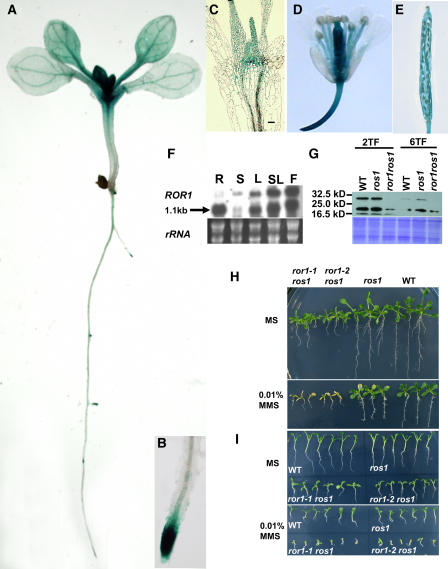
Figure 8.
The Expression Pattern of ROR1/RPA2A and Sensitivity of ror1 ros1 to MMS.
(A) to (E) GUS analysis in Arabidopsis transgenic seedlings. The complemented seedlings obtained from Figure 7 were used for the GUS activity assay.
(A) The overall expression within a young seedling.
(B) Expression within a primary root apex.
(C) Expression within shoot apex tissues in median longitudinal sections.
(D) Expression within a flower.
(E) Expression within a silique.
(F) RNA gel blot analysis of ROR1/RPA2A expression in different tissues. R, root; S, stem; L, leaf; SL, stem leaf; F, flower. rRNA was used as a loading control.
(G) Protein gel blot analysis of ROR1/RPA2A expression in seedlings with different true leaves. Forty micrograms of total proteins was loaded in each lane. 2TF, seedlings with two true leaves; 6TF, seedlings with six true leaves. WT, C24 wild type.
(H) The seedlings of ror1-1 ros1 and ror1-2 ros1 are more sensitive to MMS than ros1. Seven-day-old seedlings were transferred to liquid MS (top panel) or liquid MS medium containing 0.01% MMS (bottom panel). The picture was taken after transferring for 5 d. Note that the growth of ror1-1 ros1and ror1-2 ros1 was seriously inhibited compared with ros1 or the wild type. WT, C24 wild type.
(I) Germination of ror1-1 ros1 and ror1-2 ros1 seeds is more sensitive to MMS. Seeds were germinated on MS (top panel) or MS containing 0.01% MMS (bottom panel) for 12 d. WT, C24 wild type.