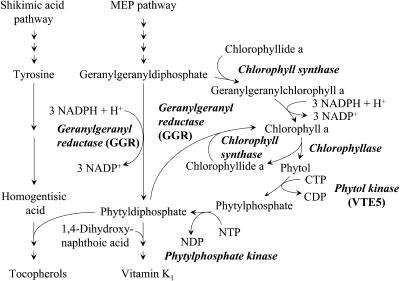
Figure 1.
Schematic Drawing of the Tocopherol Biosynthetic Pathway.
The metabolic fate of GGDP is shown in detail. Enzyme designations are shown in italicized bold text. GGDP is proposed either to be directly reduced by GGR to PDP or to serve as substrate for chlorophyll synthase to form geranylgeranyl chlorophyll a. GGR reduces geranylgeranyl chlorophyll a to form chlorophyll a. Hydrolysis of chlorophyll by the action of chlorophyllase releases phytol, which can be reassimilated through two subsequent phosphorylation reactions with phytol kinase (VTE5) catalyzing a CTP-dependent phosphorylation of free phytol. Another enzyme, phytylphosphate kinase, is proposed for the second phosphorylation reaction to obtain PDP. PDP can enter the tocopherol biosynthetic pathway, be utilized for chlorophyll biosynthesis, or enter vitamin K (phylloquinone) biosynthesis. MEP, methylerythritol phosphate pathway.