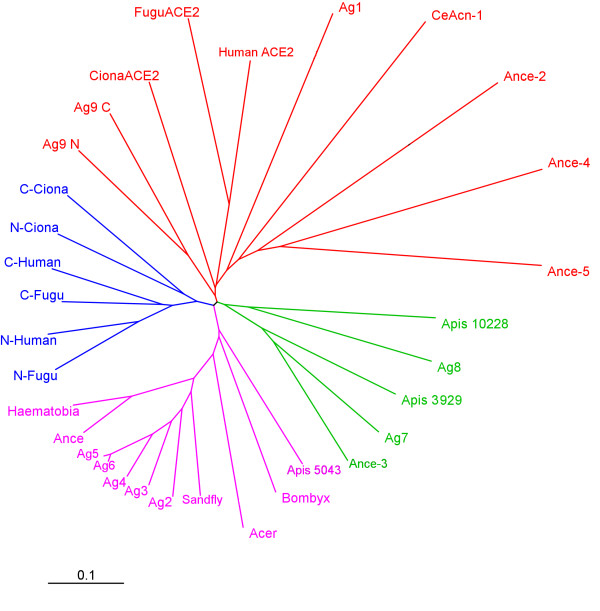
Figure 5.
Evolutionary relationships of invertebrate and chordate ACE-like proteins. Core sequences (corresponding to amino acids161 to 569 of the AnoACE2 pre-protein) of each protein were aligned and a neighbour-joining tree calculated using CLUSTALX [36]. TreeView was used to produce a radial tree. Sequences used were AnoACEs (Ag)1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 (N and C domains); D. melanogaster ANCE, ACER, ANCE-2, -3, -4 and -5; B. mori ACE (accession no. BAA97657); H. irritans ACE (accession no. Q10715); C. elegans ACN-1; N and C domains of Human ACE, Fugu rubripes (Ensembl SINFRUP00000174092) ACE; A. mellifera Ensembl proteins ENSAPMP00000005043, ENSAPMP00000003929 and ENSAPMP000000010228; Sandfly (Lutzomyia longipalpis) ACE (accession no. AAS16911); Human and F. rubripes (Ensembl SINFRUP00000161972) ACE2. N and C domains of Ciona intestinalis ACE, were assembled from genomic sequence in contig AABS01000302.1. Scale bar shows number of amino acid substitutions per site.