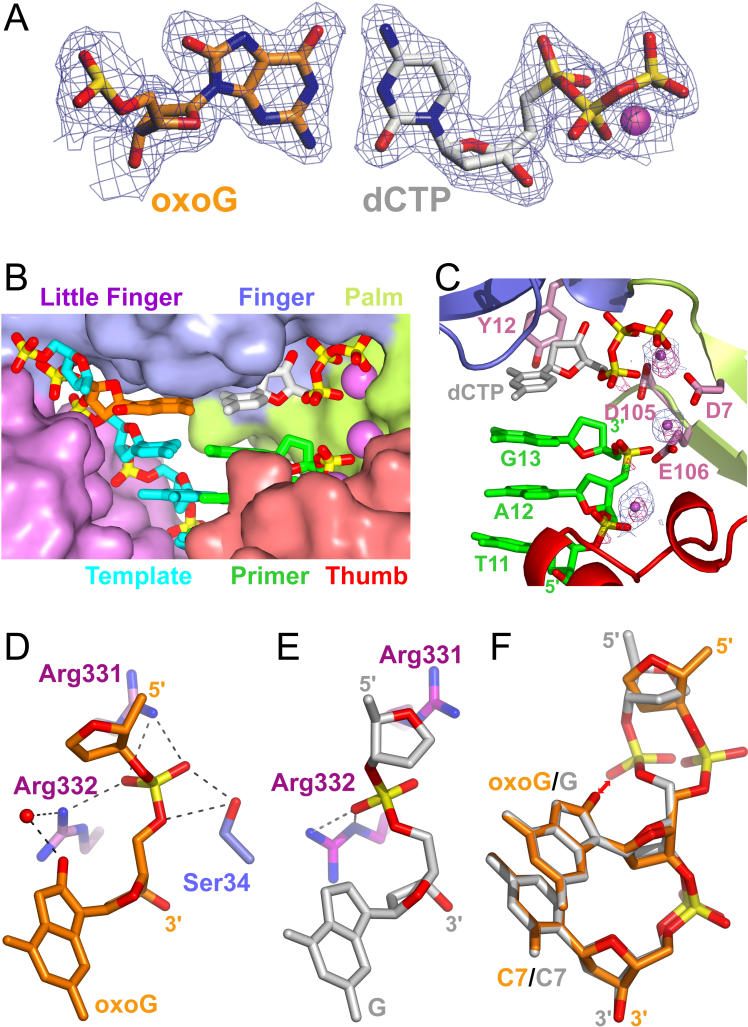
Figure 3. Comparison of Pairing Alignments and Intermolecular Interactions Involving oxoG-Modified and Unmodified G Residues in Insertion Ternary Complexes with Incoming dCTP.
(A) oxoG(anti) paired with dCTP(anti) in the oxoG-modified insertion ternary complex, with a coordinated Ca2+ cation. 2Fo-Fc 1.95 Å electron density map contoured at 1σ level (1.95 Å resolution).
(B) Shape-complementarity between incoming dNTP and the Dpo4 active site pocket containing two chelated Ca2+ cations (pink spheres). The dCTP (in silver) is aligned opposite oxoG lesion (in gold).
(C) Distinguishing Ca2+ from Mg2+ ions in the Dpo4 oxoG-modified insertion ternary complex. Strong peaks, contoured in pink at 5 σ level, are found in the 2.0 Å anomalous map plotted for a dataset collected at 1.5418 Å wavelength (Mg2+ cation has a much weaker anomalous scattering at this wavelength than Ca2+ cation). 2Fo-Fc electron density map for Ca2+ cations contoured in blue at 3 σ level are shown by small pink spheres.
(D) Interactions between oxoG nucleotide and amino acid side chains of Dpo4 in the oxoG-modified insertion ternary complex.
(E) Interactions between G nucleotide and amino acid side chains of Dpo4 in the unmodified G insertion ternary complex.
(F) Comparison of the phosphate backbone conformation of C5-oxoG6-C7 (gold) and unmodified C5-G6-C7 (gray) segments within the Dpo4 active site of their respective insertion ternary complexes.