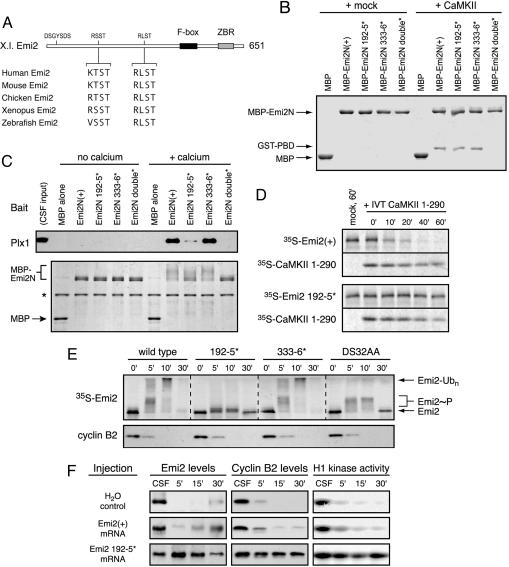
Fig. 3.
Emi2's 192RSST motif is critical for CaMKII-induced Plx1 association and is required for Emi2 destruction and CSF release. (A) A schematic of the primary structure of Xenopus Emi2 with candidate CaMKII target/Polo Box-binding sites and equivalent sequences among vertebrate Emi2 orthologs depicted. (B) Both the 192RSST and 333RLST motifs of Emi2 can bind the PBD in vitro after phosphorylation by CaMKII. Indicated variants of the Emi2 N terminus were phosphorylated by CaMKII and processed as in Fig. 2B to assay Polo Box-binding. (C) The 192RSST motif of Emi2 is chiefly responsible for Ca2+-induced Plx1 association in CSF extract. Indicated variants of the Emi2 N terminus were incubated in CSF extract for 5 min with or without Ca2+ addition. Recombinant protein was purified on amylose resin, electrophoresed, and Coomassie stained. Associated Plx1 was detected by immunoblotting. (D) CaMKII-induced Emi2 destruction requires the 192RSST motif of Emi2. Radiolabeled IVT Emi2 was preincubated in CSF extract for 5 min before addition of IVT-active CaMKII fragment or mock IVT. Emi2 stability was monitored by autoradiography. (E) The 192RSST motif in Emi2 is required for Ca2+-induced Emi2 destruction in CSF extract. Radiolabeled IVT Emi2 variants were incubated in CSF extract with Ca2+ addition, and Emi2 stability and gel mobility were monitored by autoradiography. (F) Expression of the Emi2 192–5* mutant in intact oocytes prohibits Ca2+-induced CSF release and meiotic exit. Oocytes were injected with in vitro-transcribed myc-Emi2 mRNA, matured with progesterone, and treated with ionophore A23187 at 3 h post-germinal vesicle breakdown to induce Ca2+ release and meiotic exit. Anti-Emi2 or anti-myc antibodies were used to detect endogenous or expressed Emi2, respectively, and cyclin B levels and H1 kinase activity were monitored at 5, 15, and 30 min after ionophore treatment.