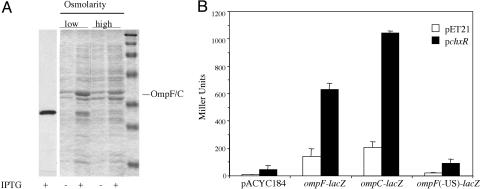
Fig. 2.
ChxR activates transcription of ompF and ompC in E. coli.(A) Coomassie brilliant blue-stained SDS/polyacrylamide gels of outer-membrane preparations of E. coli before and after induction of ChxR expression by IPTG. The outer membranes were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. E. coli harboring pChxR were grown in LB (low osmolarity) or LB containing 20% sucrose (high osmolarity) at 37°C until a OD600 of ≈0.6. No IPTG or 1 mM IPTG was added, and cells were grown for an additional 2 h before centrifugation. The first lane is an immunoblot showing induction of ChxR. The antibody used for detection is anti-hexaHIS. The molecular mass markers are 202, 116, 94, 53, 37, 29, and 20 kDa. (B) β-Galactosidase assays measured transcriptional activity from ompF–lacZ and ompC–lacZ fusions after induction of strains containing the vector alone (pET21) or chxR (pChxR). Little activity was detected in an ompF–lacZ fusion in which the upstream regulator sequences had been removed [ompF(-US)-lacZ].