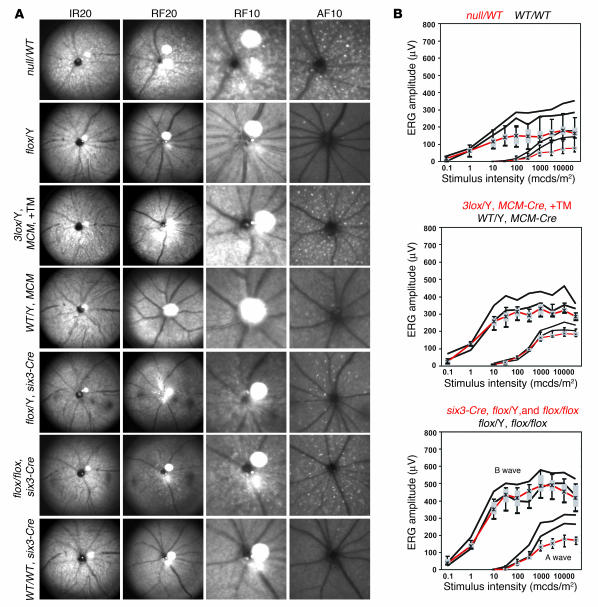
Figure 3.
Ophthalmic and electroretinographic analysis of Chm mutant mouse eyes. (A) Retinal SLO images from representative Chm mutant animals. The Chm alleles, MerCreMer (MCM) transgene, six3-Cre transgene, and TM induction (+TM) are indicated to the left of each set of panels. An equipment setting of 20° was used for a full view and of 10° for a more detailed view. The wavelengths shown are infrared (890 nm and 20°, IR20), green (514 nm and 20° or 10°, RF20 and RF10), and blue autofluorescence (488 nm with barrier at 500 nm and 10°, AF10). (B) Electroretinographic analysis showing a and b waves for the indicated strains of mice. Box and whisker plot of mutant mouse data (red) (whiskers 5% and 95% quantile, box 25–75% quantile, asterisk median) in comparison with respective control mouse data (black) (5% and 95% quantiles indicated by the lower and upper black lines, respectively, delimiting a 90% normal range). mcds, millicandela seconds.