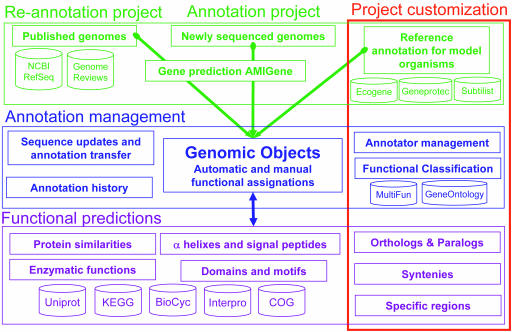
Figure 2.
Simplified PkGDB relational model. PkGDB is made of three main components: sequence and annotation data (in green), annotation management (in blue) and functional predictions (in purple). Sequences and annotations come from three sources namely public databanks, sequencing centers and specialized databases focused on model organisms. For genomes of interest, a (re)-annotation process is performed using AMIGene (19) and leads to the creation of new ‘Genomic Objects’. Each ‘Genomic Object’ and associated functional prediction results are stored in PkGDB. The database architecture supports integration of automatic and manual annotations, and management of a history of annotations and sequence updates. The core of PkGDB can be supplemented by other tables to take into account genome project specificities (‘Project customization’, red rectangle).