Figure 2.
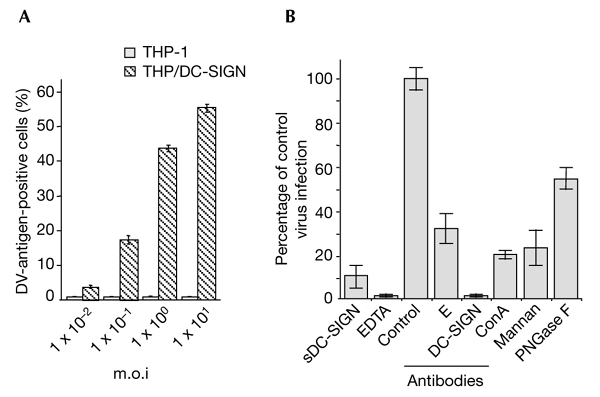
The lectin DC-SIGN is crucial for the entry of dengue virus into monocytic cells. THP-1 and TPH/DC-SIGN cells infected with dengue virus (DV)-1 FGA/NA d1d were analysed for viral protein production as described in the legend for Fig. 1. (A) Cells infected at various multiplicities of infection (m.o.i.s) were analysed using an immunofluorescence assay. (B) THP/DCsIGN cells were infected with FGA/NA d1d virus at m.o.i.s of 5 (columns labelled EDTA and antibodies) or 1 (columns labelled sDC-SIGN, mannan and ConA). Before infection, THP/DC-SIGN cells were incubated with either 20 µg ml−1 mannan, 5 mM EDTA, 20 µg ml−1 monoclonal antibody BD12.5 (control), a 1:50 dilution of monoclonal antibody 9D12 (E), or 20 µg ml−1 monoclonal antibody 1B10 (against DC-SIGN) as described in the legend to Fig. 1. FGA/NA d1d virus (1 × 105 AP61 focus-forming units) was mixed with 10 µg ml−1 sDCsIGN (20 min at 25 °C) or incubated with 25 µg ml−1 ConA (1 h at 37 °C) or N-glycosidase F (PGNase F; see the Methods section). Cells positive for DV antigens are expressed as a percentage of untreated, DV-infected THP/DC-SIGN cells (percentage of control virus infection). ConA, concanavalin A; DC-SIGN, dendritic-cell-specific ICAM 3-grabbing non-integrin; sDC-SIGN, the soluble, tetrameric ectodomain of DC-SIGN.
