Figure 3.
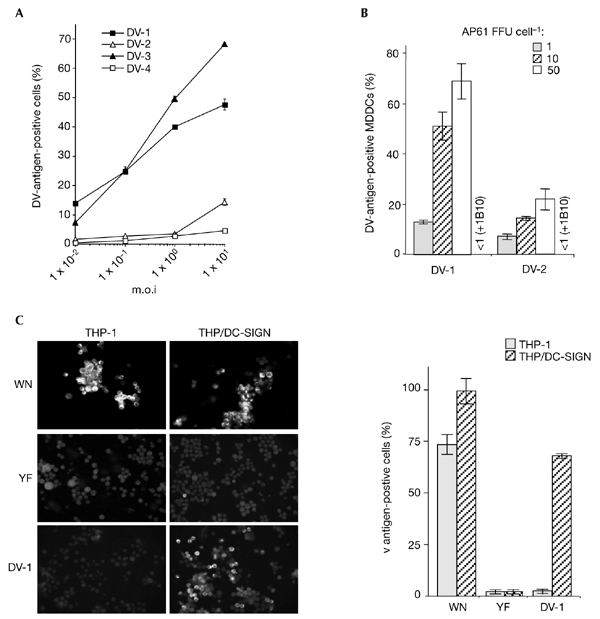
Flavivirus infectivity in DC-SIGN-expressing monocytic cells. Cells infected with flaviviruses were assayed 25 h (monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MDDCs)) or 40 h (THP/DC-SIGN) post-infection. for the presence of viral antigens, using the immunofluorescence assay described in the legend of Fig. 1. (A) THP/DCsIGN cells were infected with strain FGA/NA d1d of dengue virus (DV)-1, the Jam strain of DV-2, strain H-87 of DV-3 or strain H-241 of DV-4, at various multiplicities of infection (m.o.i.s) (B) MDDCs were infected with highly purified DV-1 FGA/NA d1d and DV-2 Jam viruses at various m.o.i.s. Before infection, MDDCs infected at an m.o.i. of 10 were incubated with 20 mg ml−1 monoclonal antibody 1B10 (+1B10), as described in the legend for Fig. 1. Experiments were performed twice using two MDCC donors. The results of one representative experiment are shown. (C) THP-1 and THP/DCsIGN cells were infected with strain IS-98-ST1 of West Nile (WN) virus (m.o.i. of 5), vaccine strain 17D of yellow fever (YF) virus (m.o.i. of 50) or DV-1 (m.o.i. of 5) and viral antigens were visualized by immunofluorescence assays with specific hyperimmune mouse ascites fluids. Each experimental point represents the mean ± s.d. of results obtained from three chambers. Magnification in left panel of (C), x100. DC-SIGN, dendritic-cell-specific ICAM3-grabbing non-integrin.
