Figure 1.
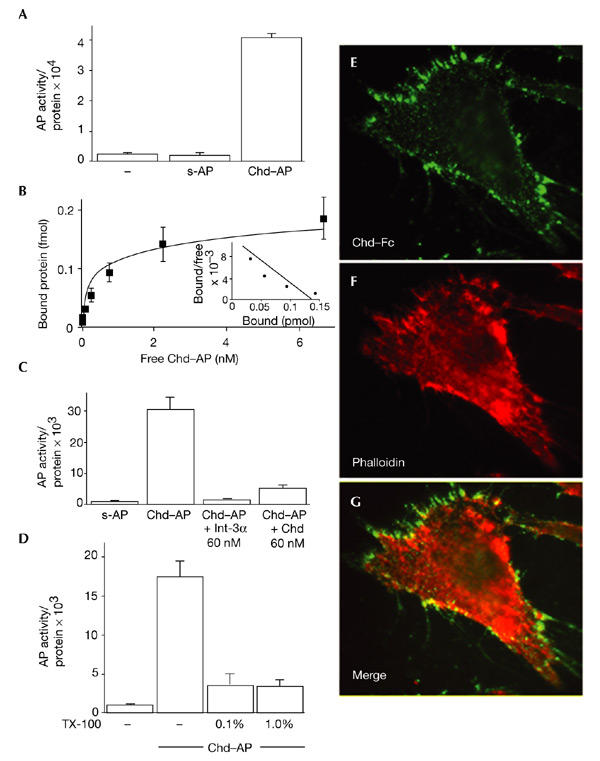
Chordin binds to the cell surface. (A) Chordin–alkaline-phosphatase (Chd–AP) binds to COS-7 cells. COS-7 cells were incubated with Chd–AP or secreted AP (s-AP) for 2 h at 4 °C, and the amount of activity of bound AP was quantified using a fluorescent AP substrate. Equal loading was confirmed by protein measurements. (B) Binding curve and Scatchard analysis of Chd–AP binding to COS-7 cells. A dissociation constant (Kd) of 0.24 nM was estimated. (C) COS-7 cells were incubated with Chd–AP in the presence of 60 nM recombinant Integrin-α3 (Int-α3; Chemicon) or mouse Chd (R&D Systems), and the amount of bound Chd–AP was quantified using a fluorescent AP substrate. Other cysteine-rich-repeat-containing proteins were not tested because they are not available in purified form. (D) Chd binding requires an intact cell membrane. COS-7 cells were incubated with 0.1% or 1.0% Triton X-100 (TX-100), and Chd–AP was bound and quantified. (E) Chd binding colocalizes with actin filaments. 10T1/2 fibroblasts were incubated with pure Chd–Fc at 4 °C, fixed and permeabilized, and binding was visualized with an anti-human IgG antibody conjugated to Alexa Fluor 486. (F) The same cell as in (E), stained with phalloidin-Alexa558 to visualize actin. (G) Merge of (E) and (F). Note the overlap between Chd–Fc and actin (yellow).
