Figure 1.
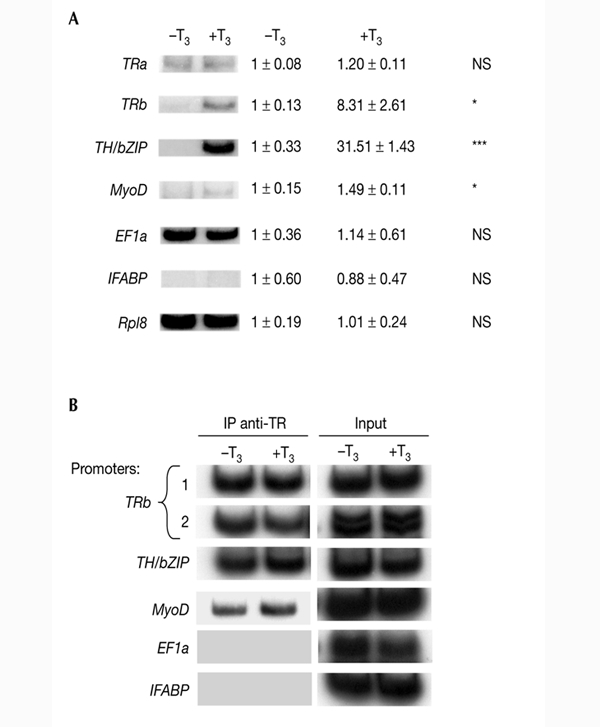
Effects of T3 on transcription and DNA binding by thyroid hormone receptor at T3-response genes in pre-metamorphic stage NF55 tadpole tail. (A) T3 induces transcription of T3-response genes. Tadpoles were treated for 48 h with 10 nM T3. Total RNA was extracted from tail tissue and used for RT–PCR (PCR after reverse transcription) analysis of thyroid hormone receptor b (TRb), TH/bZIP (a basic leucine-zipper TH-response gene), MyoD, intestinal fatty acid binding protein (IFABP), elongation factor 1a (EF1a) and ribosomal protein L8 (Rpl8) expression. The internal control was Rpl8. The results were also quantified by phosphoimager scanning. The average values ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments are expressed as multiples of induction, where 1 is equal to expression in the absence of T3 (control level). For each sample, densitometry readings were normalized against the value for Rpl8 RNA (except for the Rpl8 data, which were not normalized). Statistical significance as compared with untreated animals is indicated as NS (not significant), * (p < 0.05) or *** (p < 0.001). (B) T3 does not affect TR binding to T3 response elements. Chromatin isolated from tails of T3-treated tadpoles (10 nM T3 for 48 h) was immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibodies against TR and analysed by PCR. Aliquots of the chromatin taken before immunoprecipitation were used directly for PCR as a control (input). For TRb promoters, we distinguished two sequences containing T3REs (sequence 1 at position +266 and sequence 2 at positions −800 to −500). All experiments were carried out at least three times. T3, thyroid hormone (triiodothyronine).
