Figure 3.
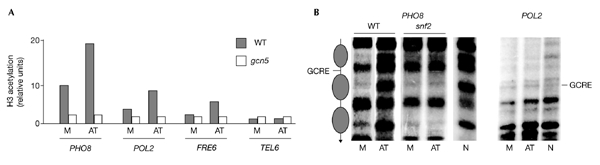
Functional consequences of coactivator recruitment. (A) Gcn5-dependent acetylation of nucleosomal histones located at the regions indicated was measured at low (M) or high (AT) Gcn4 concentrations by chromatin immunoprecipitation using antibodies raised against a diacetylated form of histone H3. Numbers indicate the enrichment of the DNA relative to a telomeric region (TEL) and corrected for the level of amplification achieved using input DNA. TEL (Vogelauer et al., 2000) was used as a control as it is heterochromatic and therefore under-acetylated. (B) The diagram in the left panel shows the mapped positions of nucleosomes around the Gcn4-response element (GCRE) site of the PHO8 gene. Gcn4-dependent remodelling of the nucleosomes positioned on either side of the GCRE located in the PHO8 open reading frame is shown in the left panel. Remodelling was monitored in wild-type (WT) or snf2 strains by determining the sensitivity to micrococcal nuclease and indirect end-labelling. M and AT indicate cells with low and high amounts of Gcn4, respectively. N is the micrococcal-nuclease cleavage pattern of naked DNA. By contrast, similar experiments for the POL2 site (right panel) showed the absence of positioned nucleosomes, as indicated by the identical patterns of micrococcal nuclease cleavages in nuclear (M and AT) or naked (N) DNA.
