Figure 1.
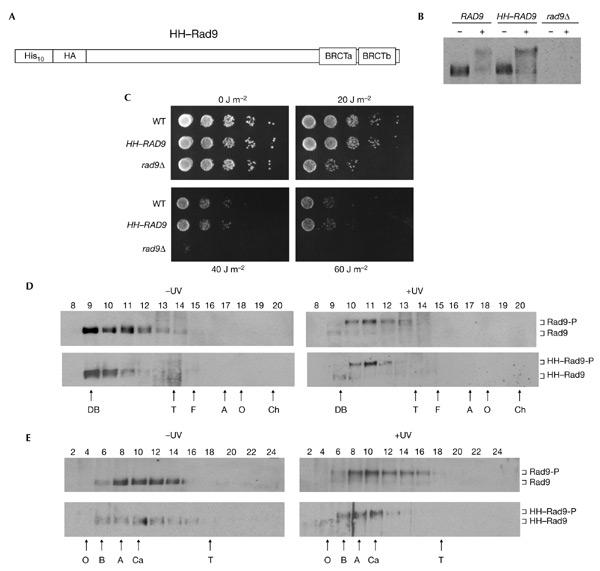
Characterization of epitope-tagged Rad9. (A) The relative position of the ten histidine residues, single haemagglutinin (HA) epitope and BRCA1 carboxy-terminal (BRCT) domains are indicated schematically. (B) Rad9 western blot of extracts from exponentially growing strains that were either mock treated (−) or irradiated with ultraviolet light (+). (C) Exponentially growing cells of the strains indicated were serially diluted onto YPD plates and irradiated with ultraviolet light at the doses indicated. (D) Rad9 western blot of fractions from a Superose 6 gel-filtration column loaded with crude extracts from wild-type cells. Blots from cells that were irradiated with ultraviolet light (+UV) or mock treated (−UV) are indicated. (E) Rad9 western blot of fractions from a 20–35% glycerol sedimentation gradient loaded with crude cell extracts from wild-type cells. Blots from cells that were irradiated with ultraviolet light (+UV) and mock treated (−UV) are indicated. Hyperphosphorylated and hypophosphorylated Rad9 and HH–Rad9 are indicated. The letters below the panels in (D) and (E) indicate the positions of standard proteins (masses, Stokes' radii and sedimentation coefficients are listed in the supplementary information online). A, aldolase; B, bovine serum albumin; Ch, chymotrypsinogen; DB, Dextran blue; F, ferritin; O, ovalbumin; T, thyroglobulin; WT, wild-type.
