Abstract
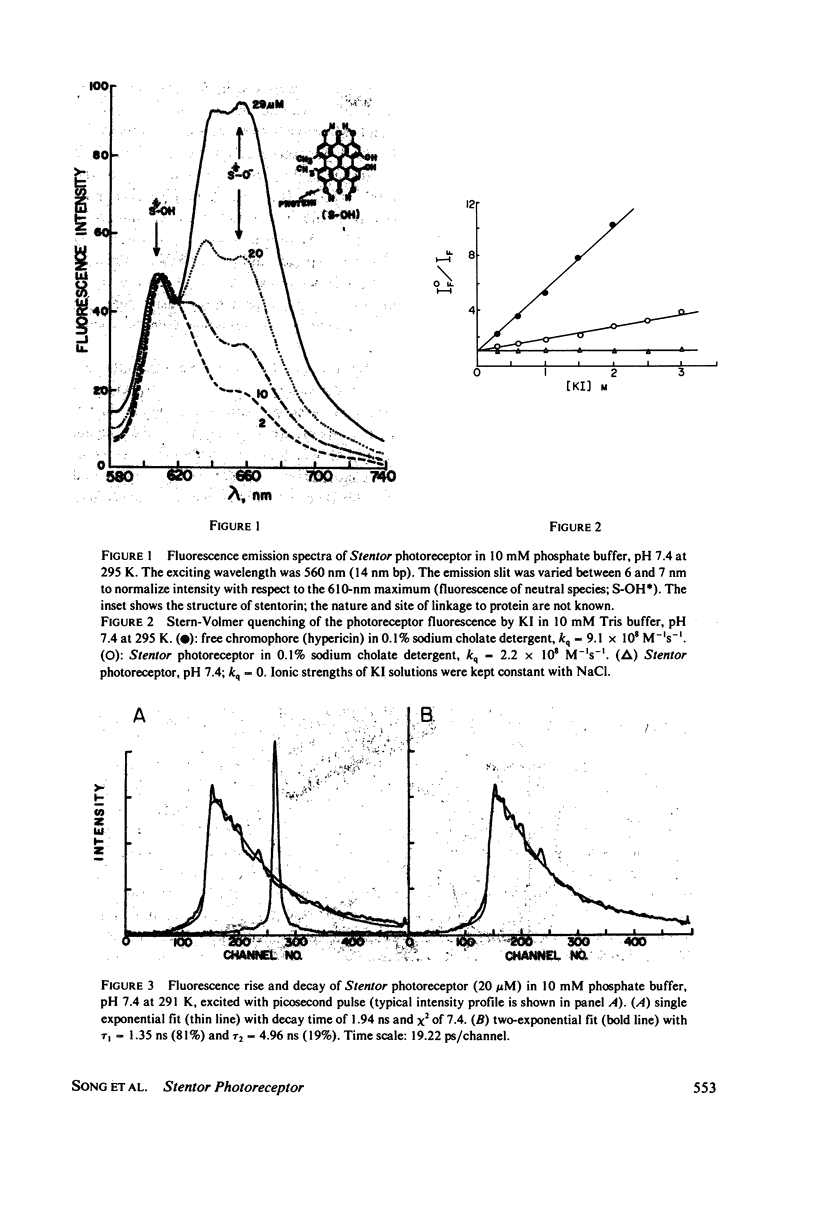
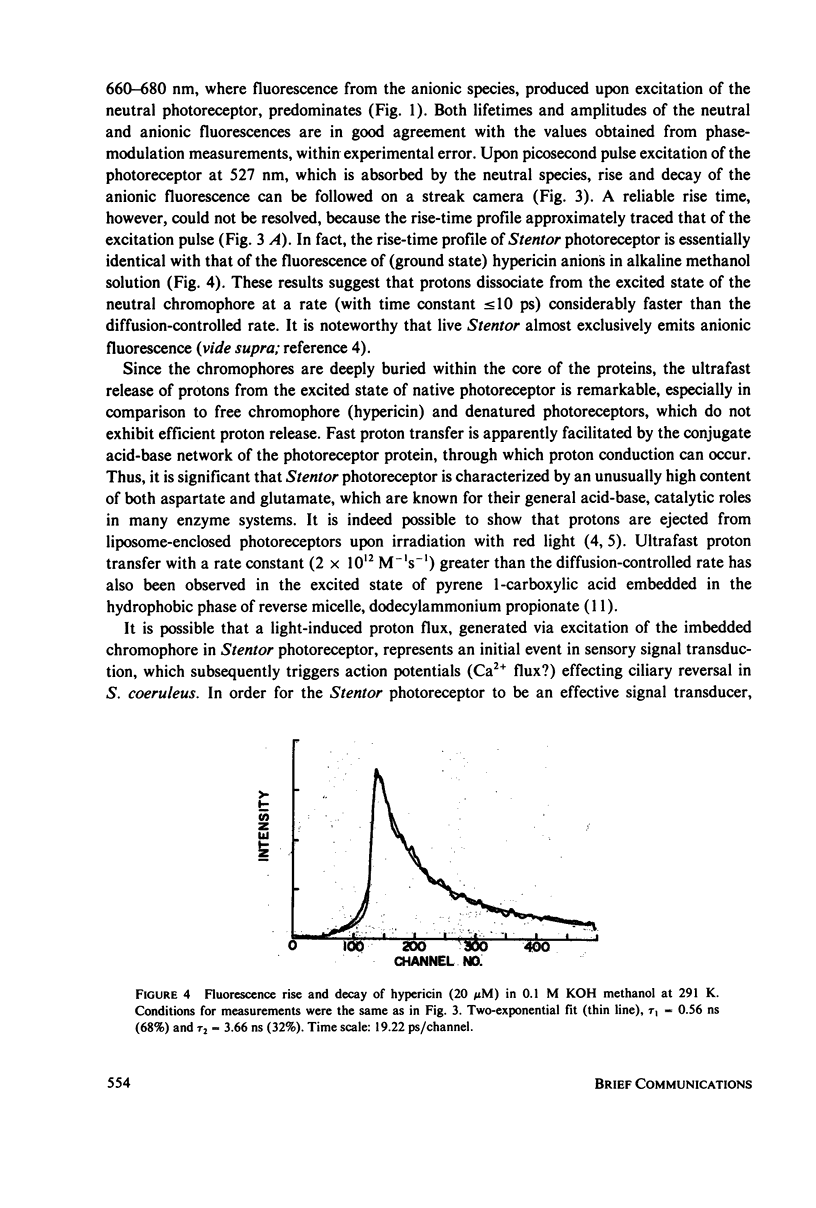
Steady-state and picosecond pulse excitations of the photophobic-phototactic receptors isolated from Stentor coeruleus produced anionic species predominantly in the excited singlet state, although neutral photoreceptors in the ground state were exclusively excited. The same photoreceptor in vivo also emits fluorescence from the excited state of its anionic species, with an excitation spectrum identical to the absorption spectrum of the neutral species in the ground state. The excited state dissociation of protons from the photoreceptor chromophore (stentorin; hypericin covalently linked to protein) efficiently occurs in less than 10 ps. A possible role of the transient-proton release from the photoreceptor, in the signal transduction photoresponse of Stentor, is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Koka P., Song P. S. The chromophore topography and binding environment of perididin.chlorophyll a.protein complexes from marine dinoflagellate algae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 20;495(2):220–231. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90379-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. B., Lee T. Y., Song P. S. Spectroscopic characterization of the Stentor photoreceptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 20;587(1):129–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. B., Yoon M., Song P. S. The pH dependence of photosensory responses in Stentor coeruleus and model system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 12;634(2):289–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


