Abstract
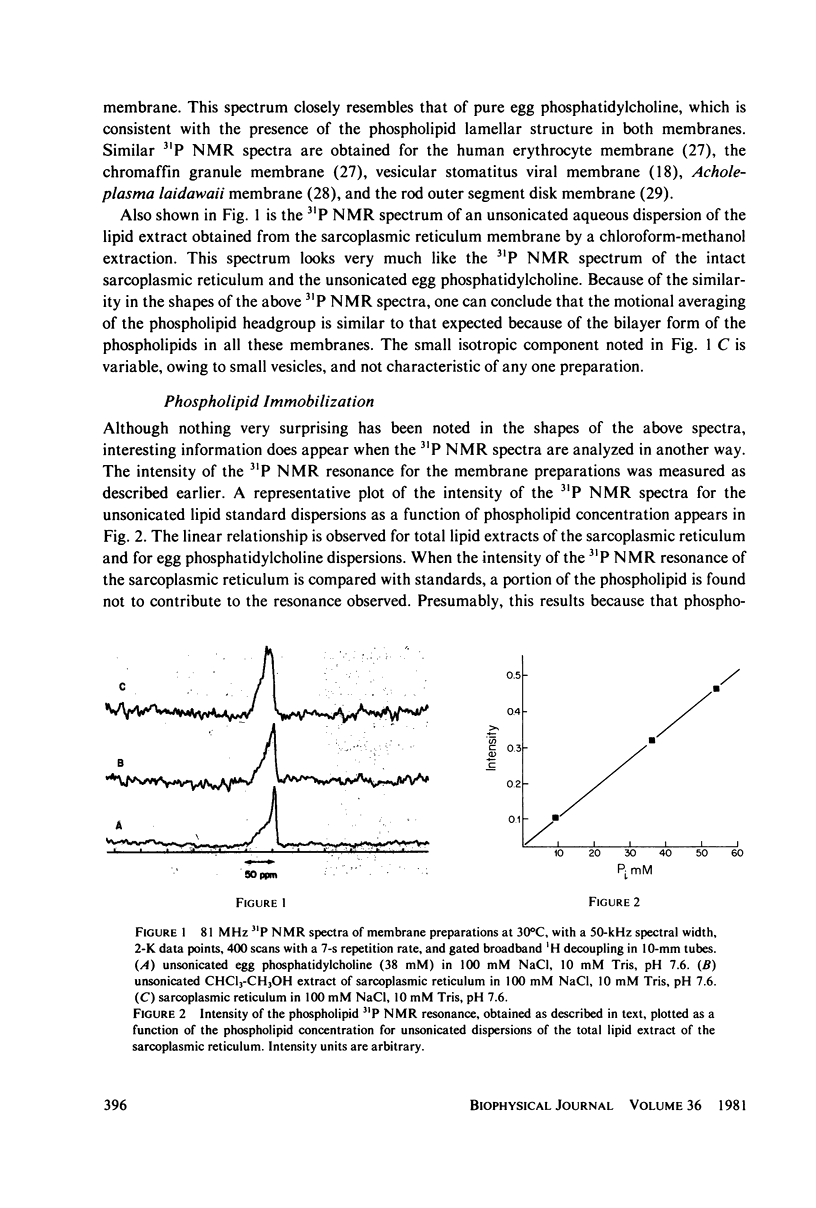
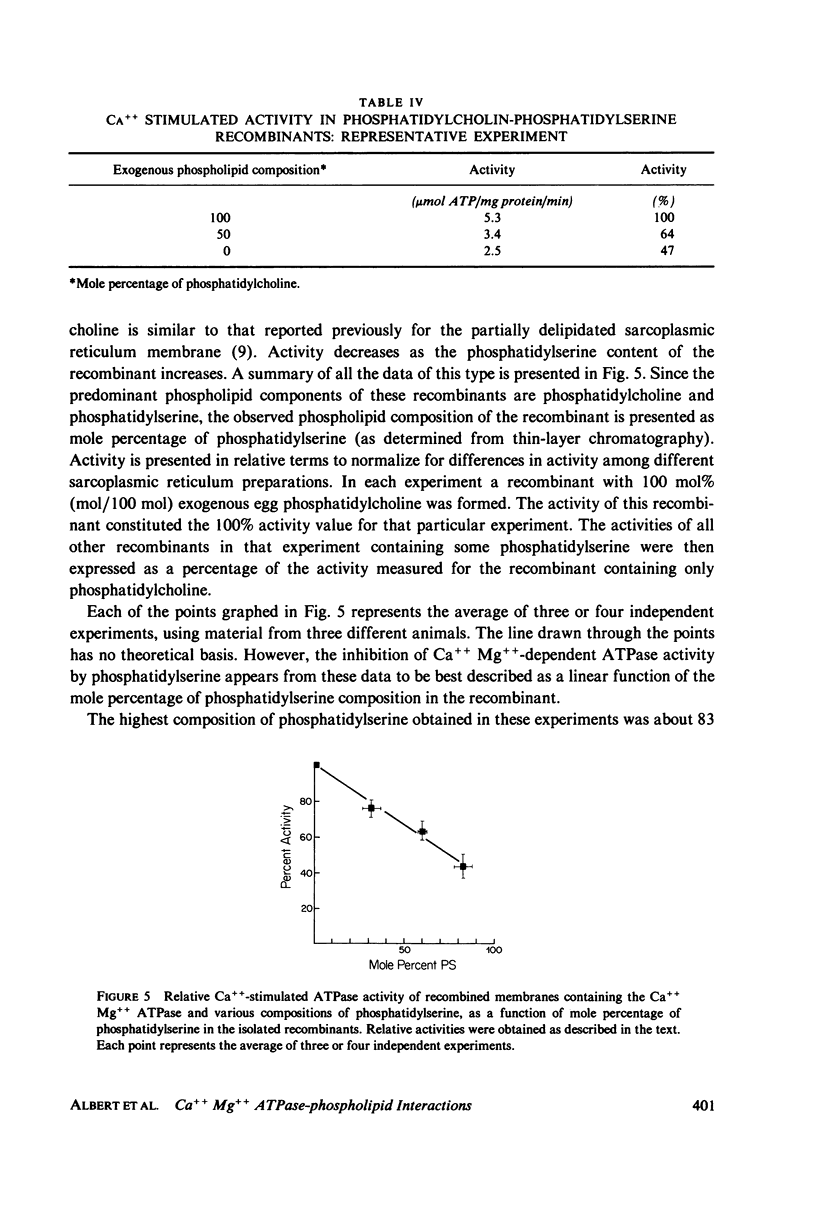
Sarcoplasmic reticulum from the white hind leg muscle of the rabbit was examined with 31P nuclear magnetic resonance as a nonperturbing probe of phospholipid-protein interactions in the intact membrane. The phospholipids of the sarcoplasmic reticulum appear to inhabit two distinct environments: one very similar in behavior to pure phospholipid lamellar dispersions and the other immobilized by the protein in the membrane. Measurement of the population of the latter environment suggests that it is dependent on salt concentration and probably not due to the Ca++ Mg++ ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This immobilization can be removed completely by papain proteolysis of the membrane protein, but only partially by trypsin treatment. The phospholipid composition of recombinants with the Ca++ Mg++ ATPase was varied in order to look for effects of the phospholipid-protein interface on enzymatic activity of the Ca++ Mg++ ATPase. Both transphosphatidylated phosphatidylethanolamine (from egg phosphatidylcholine) and bovine brain phosphatidylserine readily partitioned into the putative boundary layer, whereas under the same conditions soybean phosphatidylethanolamine was excluded. Only phosphatidylserine affected the activity of the enzyme, causing an inhibition that was proportional to the phosphatidylserine content, relative to phosphatidylcholine.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. P., Smith G. A., Houslay M. D., Hesketh T. R., Metcalfe J. C., Warren G. B. The phospholipid headgroup specificity of an ATP-dependent calcium pump. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 16;513(3):310–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Grip W. J., Drenthe E. H., Van Echteld C. J., De Kruijff B., Verkleij A. J. A possible role of rhodopsin in maintaining bilayer structure in the photoreceptor membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 12;558(3):330–337. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kruijff B., Cullis P. R., Radda G. K., Richards R. E. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance of Acholeplasma laidlawii cell membranes and derived liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 6;419(3):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean W. L., Tanford C. Properties of a delipidated, detergent-activated Ca2+--ATPase. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1683–1690. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eletr S., Inesi G. Phospholipid orientation in sarcoplasmic membranes: spin-label ESR and proton MNR studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):174–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90321-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Fernández J. C., Goñi F. M., Bach D., Restall C., Chapman D. Protein--lipid interactions. A study of (Ca2+-Mg2+)ATPase reconstituted with synthetic phospholipids. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Houslay M. D., McGill K. A., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C., Warren G. B. Annular lipids determine the ATPase activity of a calcium transport protein complexed with dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4145–4151. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Ikemoto N. Disposition of proteins and aminophospholipids in the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8446–8454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Ikemoto N., Gergely J. Role of phospholipids in the calcium-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Enzymatic and ESR studies with phospholipid-replaced membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4224–4232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H. Purification and properties of an adenosine triphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4508–4518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin A. C., Cullis P. R., Hemminga M. A., Hoult D. I., Radda G. K., Ritchie G. A., Seeley P. J., Richards R. E. Application of 31P NMR to model and biological membrane systems. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80719-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin A. C., Herbette L., Blasie J. K., Wang C. T., Hymel L., Fleischer S. 31P-NMR studies of oriented multilayers formed from isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum and reconstituted sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 22;643(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Conner G. E., Fleischer S. Isolation of sarcoplasmic reticulum by zonal centrifugation and purification of Ca 2+ -pump and Ca 2+ -binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):246–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Fleischer S. The role of phospholipid in CA 2+ -stimulated ATPase activity of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Isolation and characterization of two types of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 21;389(1):51–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90385-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore N. F., Patzer E. J., Wagner R. R., Yeagle P. L., Hutton W. C., Martin R. B. The structure of vesicular stomatitis virus membrane. A phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance approach. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):234–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Onishi S. Organization of lipids in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane and Ca2+-dependent ATPase activity. J Biochem. 1975 Nov;78(5):1039–1045. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens K., Ruth R. C., Weglicki W. B. Lipid composition of purified fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum of the rabbit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):479–481. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss-Husson F. Structure des phases liquide-cristallines de différents phospholipides, monoglycérides, sphingolipides, anhydres ou en présence d'eau. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):363–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzolo L. J., Maire M., Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Molecular weights and hydrophobicity of the polypeptide chain of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium(II) adenosine triphosphatase and of its primary tryptic fragments. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3433–3437. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzolo L. J., Maire M., Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Molecular weights and hydrophobicity of the polypeptide chain of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium(II) adenosine triphosphatase and of its primary tryptic fragments. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3433–3437. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. 13 C and 1 H nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation measurements of the lipids of sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2903–2909. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romans A. Y., Yeagle P. L., O'Connor S. E., Grisham C. M. Interaction between glycophorin and phospholipids in recombined systems. J Supramol Struct. 1979;10(2):241–251. doi: 10.1002/jss.400100213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lenard J. Membrane asymmetry. Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):743–753. doi: 10.1126/science.402030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarzala M. G., Michalak M. Studies on the heterogeneity of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 2;513(2):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance and the head group structure of phospholipids in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 31;515(2):105–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. S., MacLennan D. H. Surface particles of sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Structural features of the adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):985–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. T., Saito A., Fleischer S. Correlation of ultrastructure of reconstituted sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane vesicles with variation in phospholipid to protein ratio. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9209–9219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Houslay M. D., Metcalfe J. C., Birdsall N. J. Cholesterol is excluded from the phospholipid annulus surrounding an active calcium transport protein. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):684–687. doi: 10.1038/255684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Toon P. A., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. Reconstitution of a calcium pump using defined membrane components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):622–626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Toon P. A., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. Reversible lipid titrations of the activity of pure adenosine triphosphatase-lipid complexes. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 31;13(27):5501–5507. doi: 10.1021/bi00724a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Hutton W. C., Huang C. H., Martin R. B. Headgroup conformation and lipid--cholesterol association in phosphatidylcholine vesicles: a 31P(1H) nuclear Overhauser effect study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3477–3481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Langdon R. G., Martin R. B. Phospholipid-protein interactions in human low density lipoprotein detected by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 26;16(15):3487–3491. doi: 10.1021/bi00634a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Romans A. Y. The glycophorin-phospholipid interface in recombined systems. A 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biophys J. 1981 Feb;33(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84885-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


