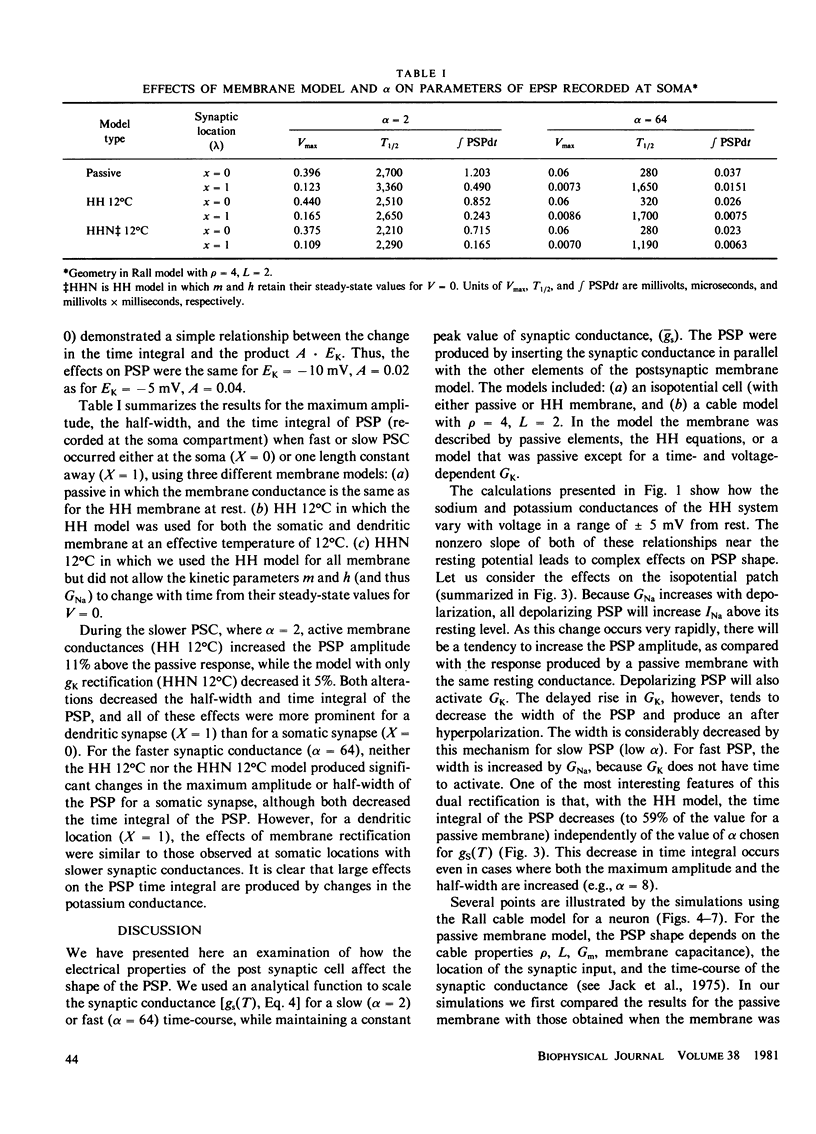
Abstract
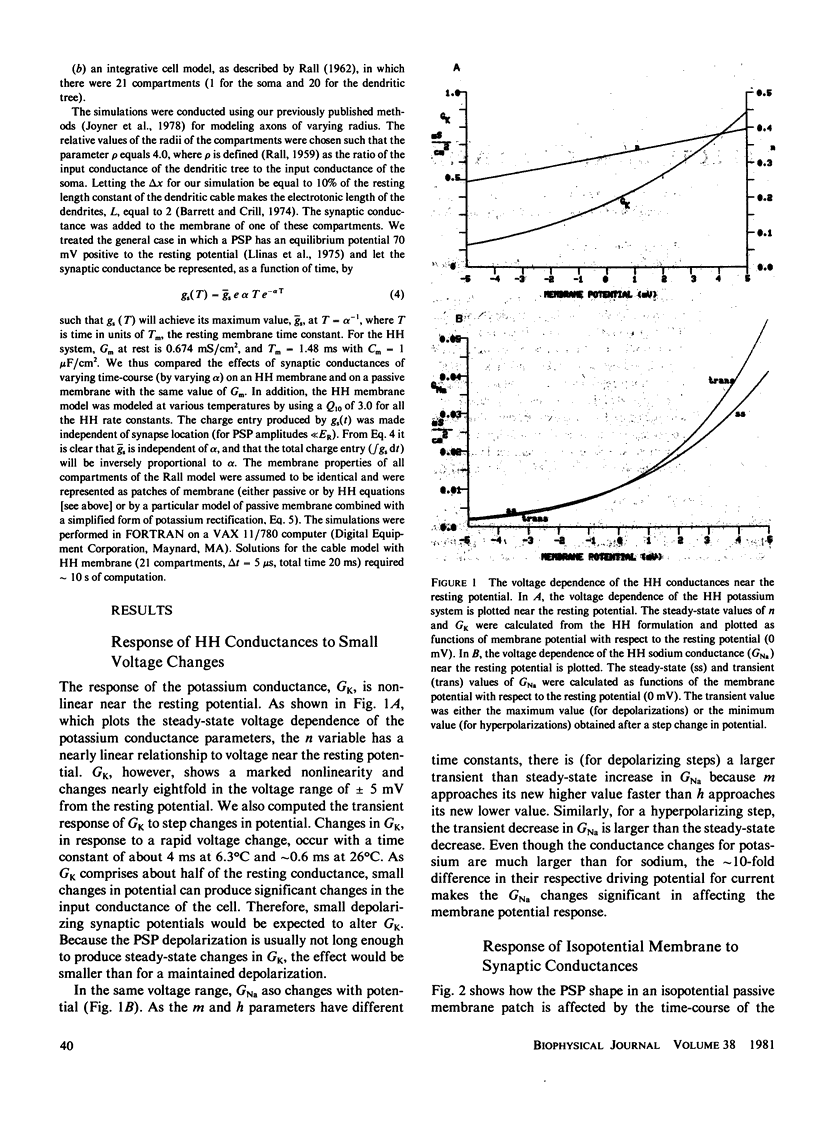
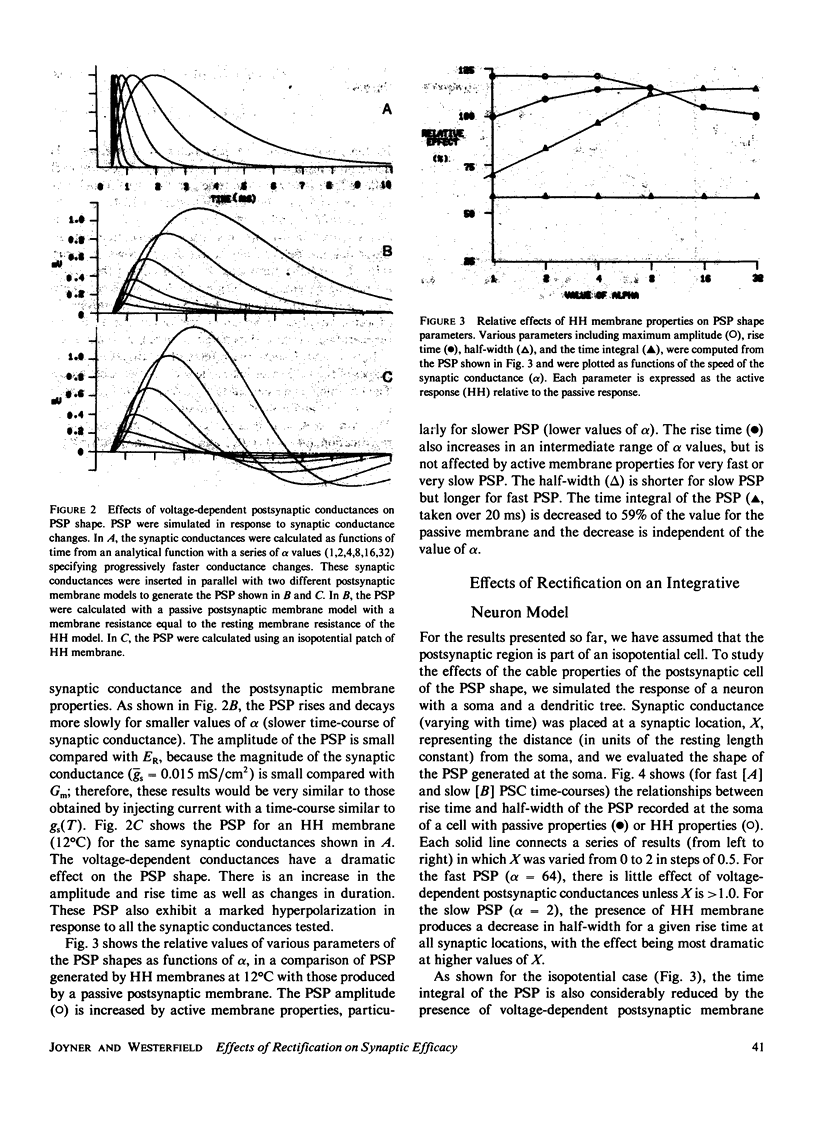
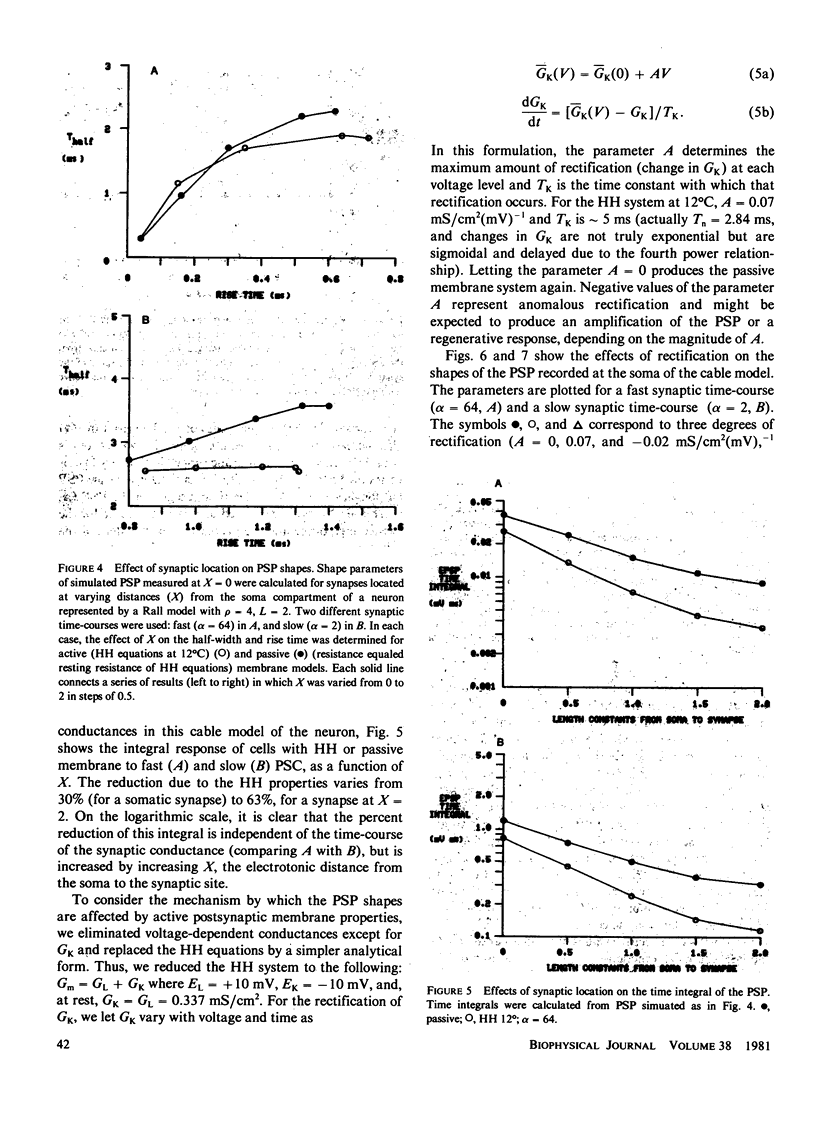
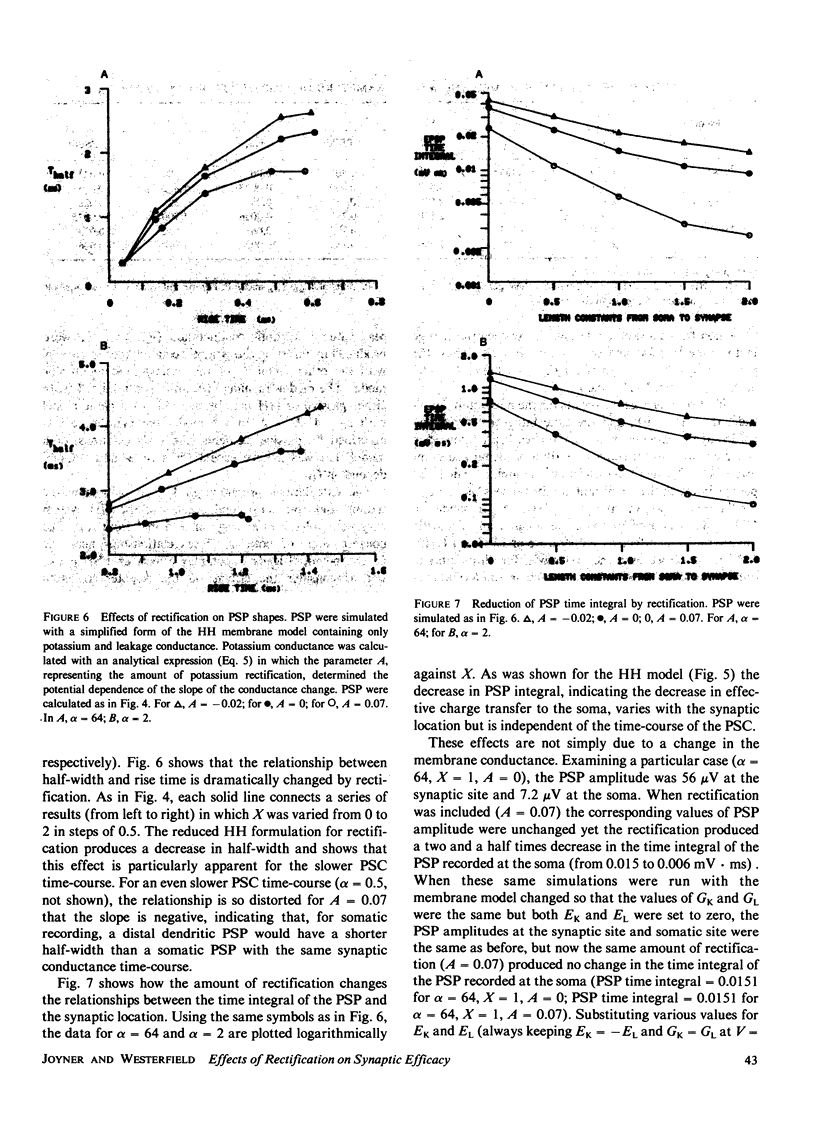
We have investigated the effects of postsynaptic membrane properties on the shape of synaptic potentials generated by time-varying synaptic conductances. We used numerical simulation techniques to model cells of several different geometrical forms, from an isopotential sphere to a neuron with a soma and a dendritic tree. A variety of postsynaptic membrane properties were tested: (a) a passive resistance-capacitance membrane, (b) a membrane represented by the Hodgkin and Huxley (HH) equations, and (c) a membrane that was passive except for a delayed rectification represented by a voltage- and time-dependent increase in GK. In all cases we investigated the effects of these postsynaptic membrane properties on synaptic potentials produced by synaptic conductances that were fast or slow compared with the membrane time constant. In all cases the effects of postsynaptic rectification occurred on postsynaptic potentials of amplitudes as low as 1 mV. The HH model (compared with the passive model) produced an increased peak amplitude (from the increase in GNa) but a decreased half-width and a decreased time integral (from the increase in GK). These effects of the HH GK change were duplicated by a simple analytical rectifier model.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Smith S. J., Thompson S. H. Ionic currents in molluscan soma. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:141–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Crill W. E. Influence of dendritic location and membrane properties on the effectiveness of synapses on cat motoneurones. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):325–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen B. N., Teubl W. P. Localization of synaptic input on dendrites of a lamprey spinal cord neurone from physiological measurements of membrane properties. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):319–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J., Poo M. M., Stuart A. E. Passive signal propagation and membrane properties in median photoreceptors of the giant barnacle. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;272(1):25–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iansek R., Redman S. J. An analysis of the cable properties of spinal motoneurones using a brief intracellular current pulse. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):613–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Miller S., Porter R., Redman S. J. The time course of minimal excitory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones by group Ia afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J. An electrical description of the motoneurone, and its application to the analysis of synaptic potentials. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):321–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner R. W., Westerfield M., Moore J. W., Stockbridge N. A numerical method to model excitable cells. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):155–170. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85481-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinhaus A. L., Prichard J. W. Close relation between TEA responses and Ca-dependent membrane phenomena of four identified leech neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;270(1):181–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Joyner R. W., Nicholson C. Equilibrium potential for the postsynaptic response in the squid giant synapse. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Nov;64(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Branching dendritic trees and motoneuron membrane resistivity. Exp Neurol. 1959 Nov;1:491–527. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Theory of physiological properties of dendrites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Mar 2;96:1071–1092. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb54120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Burke R. E., Smith T. G., Nelson P. G., Frank K. Dendritic location of synapses and possible mechanisms for the monosynaptic EPSP in motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1169–1193. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltman B. Electrical properties and fine structure of the ampullary canals of Lorenzini. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1966;264:1–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


