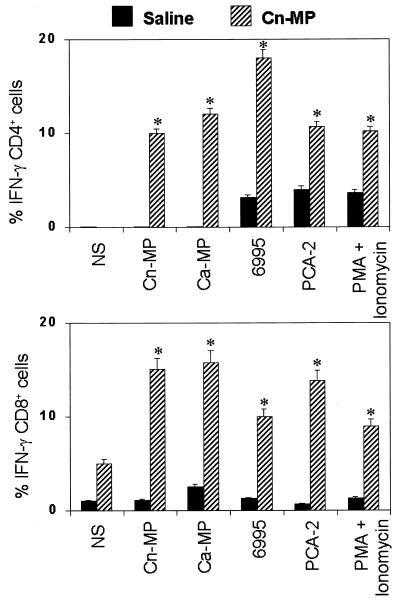
FIG. 3.
Effect of CnMP on IFN-γ synthesis from splenic T cells. Mice were treated twice with saline or CnMP (10 μg) and sacrificed 24 h later. Splenocytes (20 × 106) were recovered and cultured alone or in the presence of CnMP (2.5 μg/ml), CaMP (2.5 μg/ml), heat-inactivated C. neoformans (6995, 40 × 106 cells/ml), or heat-inactivated C. albicans (PCA-2, 40 × 106 cells/ml) for 18 h. As a positive control, cells were stimulated with 50 ng of PMA/ml and 2 mM ionomycin. Stimulations were carried out in the presence of monensin. The stimulated cells were stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 MAb and fixed with paraformaldehyde. Cells were then stained with an R-phycoerythrin-labeled anti-IFN-γ antibody in the presence of a permeabilizing agent. The stained cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for the coexistence of two different fluorescent tags in the same cell. Data are expressed as the percentages of CD4 IFN-γ (upper panel)- or CD8 IFN-γ (lower panel)-positive cells. Results represent means ± SEM of three separate experiments.∗, P < 0.05 (CnMP-treated versus saline-treated mice).