Abstract
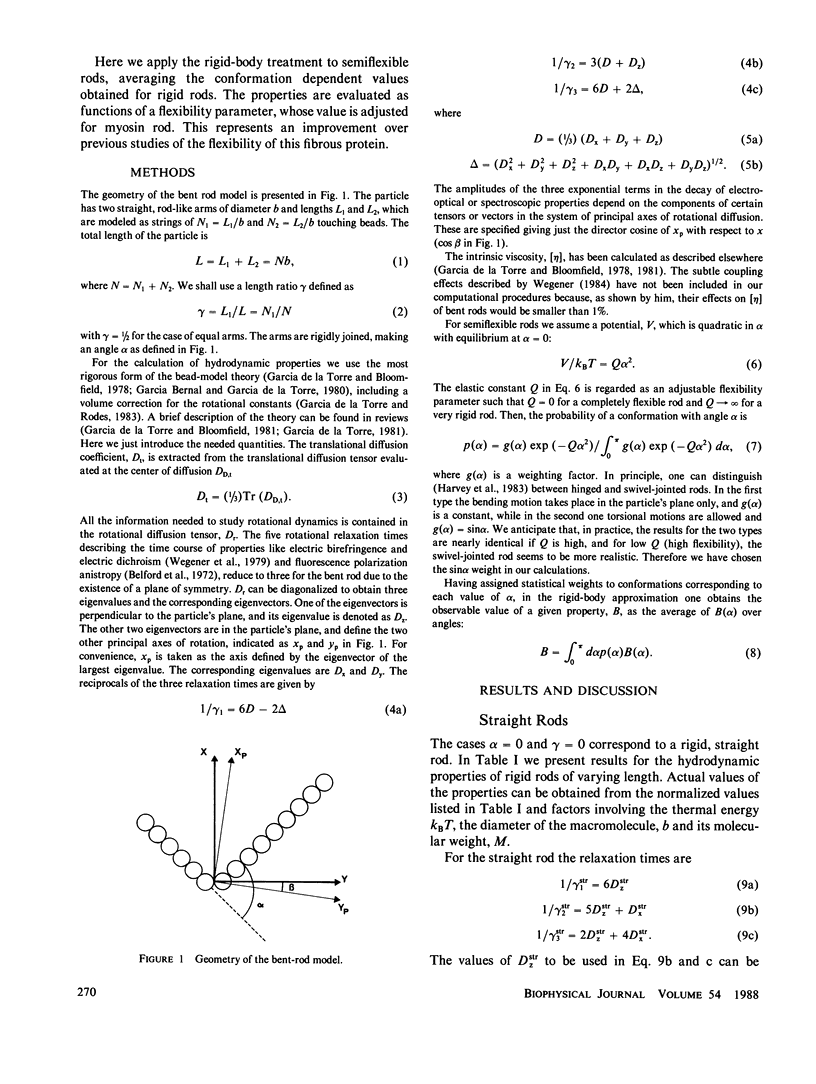
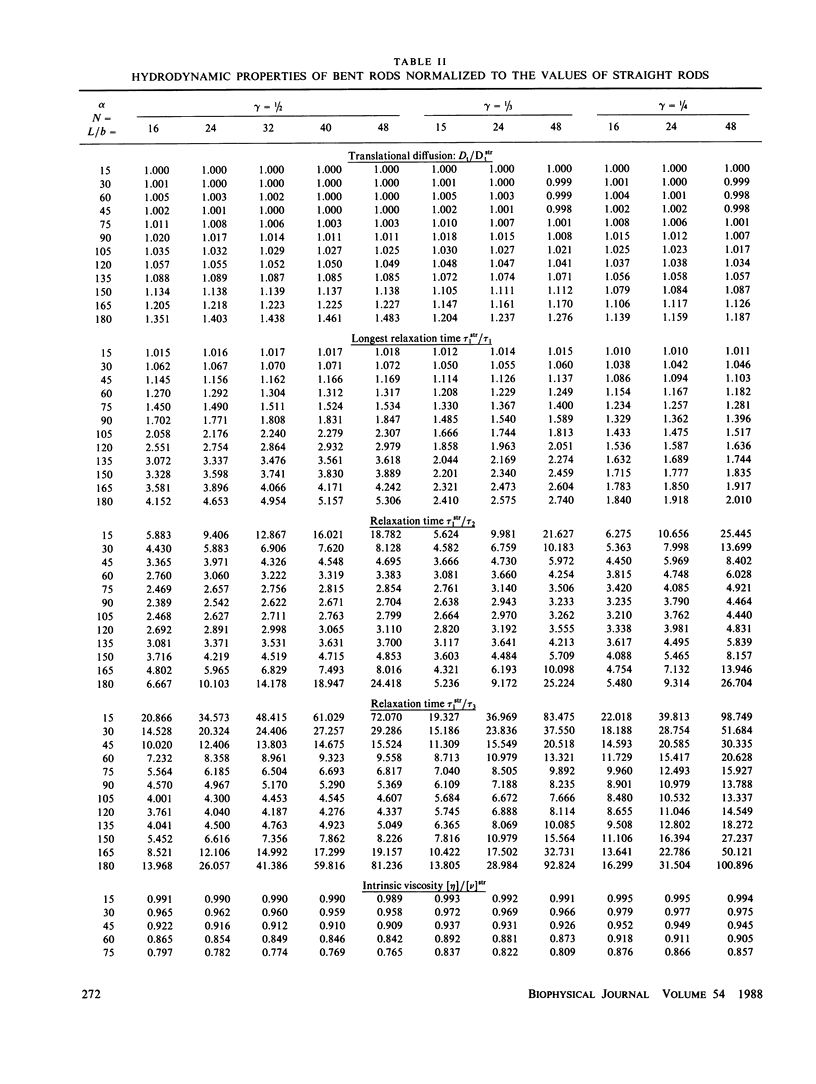
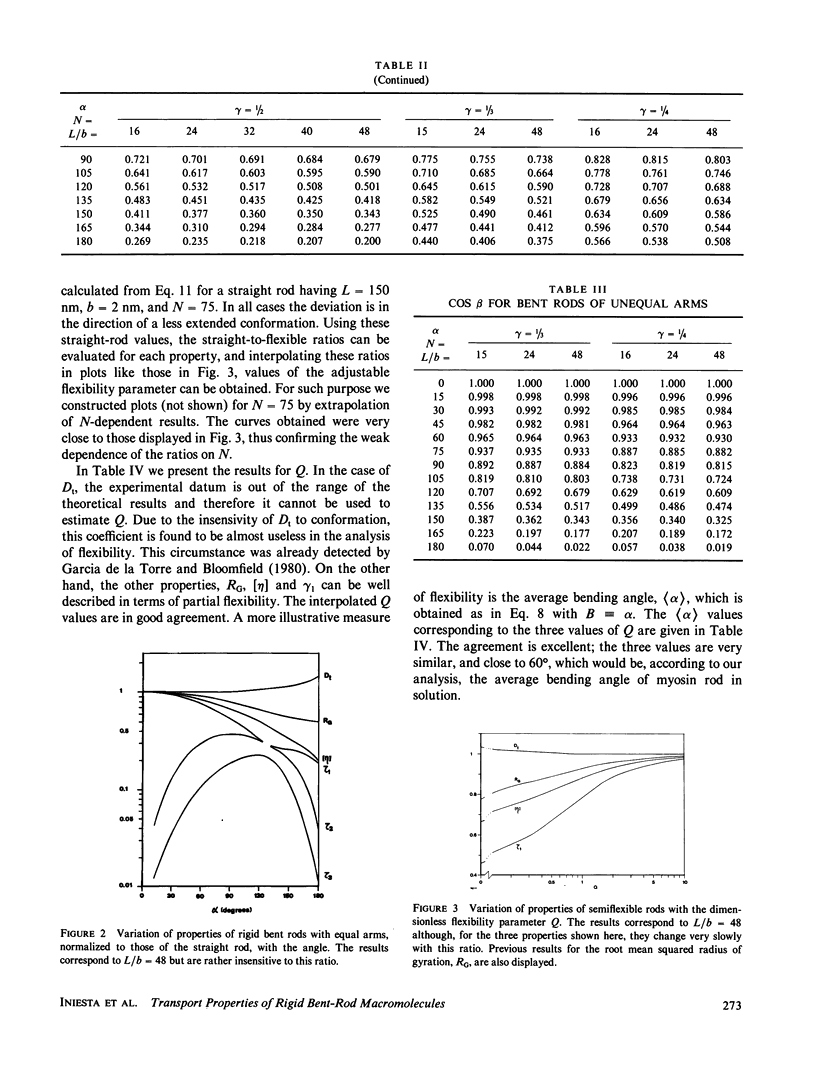
The translational diffusion coefficients, rotational relaxation times and intrinsic viscosities of rigid bent rods, composed by two rodlike arms joined rigidly at an angle alpha, have been evaluated for varying conformation using the latest advances in hydrodynamic theory. We have considered semiflexible rods in which the joint is an elastic hinge or swivel, with a potential V(alpha) = 1/2Q alpha 2 with constant Q. Accepting the rigid-body treatment, we calculate properties of broken rods by averaging alpha-dependent values for rigid rods. The results are finally used to interpret literature values of the properties of myosin rod. Q is regarded as an adjustable parameter, and the value fitted is such that the average bending angle of myosin rod is approximately 60 degrees.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belford G. G., Belford R. L., Weber G. Dynamics of fluorescence polarization in macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1392–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M., Harrington W. F. Geometry of the myosin dimer in high-salt media. II. Hydrodynamic studies on macromodels of myosin and its rod segments. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1456–1462. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardinaud R., Bernengo J. C. Electric birefringence study of rabbit skeletal myosin subfragments HMM, LMM, and rod in solution. Biophys J. 1985 Nov;48(5):751–763. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83833-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia de la Torre J. G., Bloomfield V. A. Hydrodynamic properties of complex, rigid, biological macromolecules: theory and applications. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Feb;14(1):81–139. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García de la Torre J., Bloomfield V. A. Conformation of myosin in dilute solution as estimated from hydrodynamic properties. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 28;19(22):5118–5123. doi: 10.1021/bi00563a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García de la Torre J., Mellado P., Rodes V. Diffusion coefficients of segmentally flexible macromolecules with two spherical subunits. Biopolymers. 1985 Nov;24(11):2145–2164. doi: 10.1002/bip.360241110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Evidence for the existence of stable curvature of DNA in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4632–4636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S., Kretzschmar K. M., O'Konski C. T., Morales M. F. Flexibility of myosin rod, light meromyosin, and myosin subfragment-2 in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4986–4990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S., Wang C. C., Zero K., Pecora R., Jardetzky O. Bending motions and internal motions in myosin rod. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1192–1197. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hvidt S., Chang T., Yu H. Rigidity of myosin and myosin rod by electric birefringence. Biopolymers. 1984 Jul;23(7):1283–1294. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hvidt S., Nestler F. H., Greaser M. L., Ferry J. D. Flexibility of myosin rod determined from dilute solution viscoelastic measurements. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4064–4073. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt E., Engle J., Richter H., Hörmann H. Shape, conformation and stability of fibronectin fragments determined by electron microscopy, circular dichroism and ultracentrifugation. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):109–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trybus K. M., Huiatt T. W., Lowey S. A bent monomeric conformation of myosin from smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6151–6155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. A. Viscoelasticity of rigid macromolecules with irregular shapes in the limit of overwhelming Brownian motion. Biopolymers. 1984 Nov;23(11 Pt 1):2243–2278. doi: 10.1002/bip.360231110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Stockmayer W. H. Intrinsic vescosity of a once-broken rod. J Chem Phys. 1967 Aug 15;47(4):1369–1373. doi: 10.1063/1.1712089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


