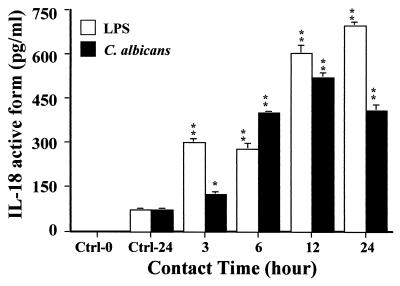
FIG. 5.
Enhanced production of active IL-18 protein by oral epithelial cells stimulated with LPS and C. albicans. Oral epithelial cells were isolated from gingival biopsy specimens of healthy persons. Cells were cultured in six-well plates alone or in the presence of C. albicans (blastospore form; 105 C. albicans cells/cm2) or LPS (5 μg/ml) for different periods of time as indicated at the bottom of the figure. Culture medium was collected from each experiment, filtered through a 0.22-μm-pore-size filter, and used to determine the amount of the active form of IL-18. IL-18 concentrations were measured by ELISA. Data are the means + SD (error bars) (n = 3). Note the basal level of IL-18 secretion by oral epithelial cells and the time-dependent increase of this cytokine caused by C. albicans infection and LPS stimulation of oral epithelial cells. The levels of significance for C. albicans and LPS-stimulated oral epithelial cell cultures compared to unstimulated cultures were P < 0.05 (∗) and P < 0.01 (∗∗), respectively. Ctrl-0 is oral epithelial cell culture medium, and Ctrl-24 is supernatant from unstimulated oral epithelial cells cultured for 24 h.