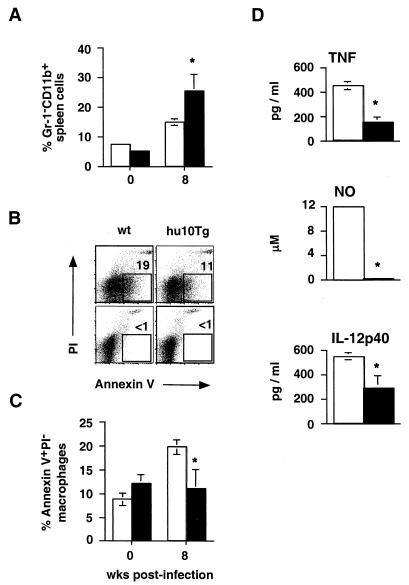
FIG. 6.
Splenic macrophages from M. avium-infected hu10Tg mice fail to undergo apoptosis and produce less TNF, NO, and IL-12p40 than their wt counterparts. Percentages of Gr-1− CD11b+ macrophages in spleens (n = 4) of wt (open bars) and hu10Tg (closed bars) mice were compared ex vivo by flow cytometry before infection and 8 weeks p.i. (A). Splenocytes from the same animals were also costained with Annexin V FITC and PI, as well as MAb to Gr-1 and CD11b to determine the percentage of apoptotic macrophages (B and C). Representative FACS profiles showing costaining of Annexin V-FITC and PI on splenic Gr-1− CD11b+ macrophages from mice at 8 weeks p.i. (B, top panels) are presented. The numbers indicate the percentages of Annexin V-FITC+ PI− Gr-1+ CD11+ cells. Preincubation of the same cells with purified recombinant Annexin V blocked Annexin V-FITC binding, confirming the specificity of the staining (B, lower panels). The mean (± SD) percentages of apoptotic macrophages (n = 4) in spleens of wt and hu10Tg mice before infection and 8 wk p.i. are shown in Fig. 6C. To measure macrophage production of proinflammatory mediators (D), T-cell-depleted, splenic adherent cells isolated from wt (open) or hu10Tg (closed) mice 2 wk after infection with M. avium were restimulated with MAVAg in vitro for 72 h. Secreted TNF and IL-12 was measured by ELISA, and NO was measured by Greiss reaction. The data shown are the means (± SD) for triplicate cultures performed on pooled cells from three animals. The significance of differences between wt and hu10Tg mice was determined using the Student t test (∗, P < 0.05).