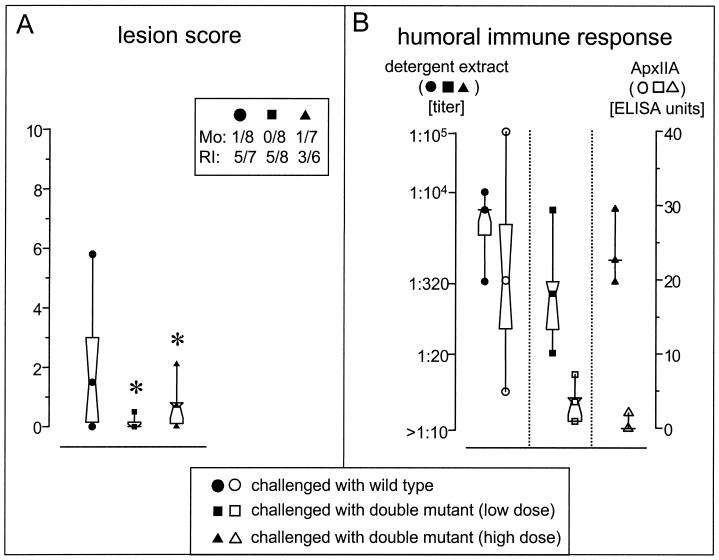
FIG. 2.
Lung lesion score (A) and humoral immune response (B) at 21 days after challenge with the A. pleuropneumoniae parent strain and isogenic double mutant. Pigs were aerosol infected with a total of 1.3 × 105 A. pleuropneumoniae C5934wt and a total of 1.3 × 105 or 6.5 × 105 A. pleuropneumoniae C5934ΔureCΔapxIIA. The aerosolization of a total of 105 bacteria results in 102 A. pleuropneumoniae per liter of aerosol in the chamber. Lung lesion scores were determined as described by Hannan et al. (12), and the bacteriological examination was done as previously described (2). Mortality (Mo) and reisolation frequency from lung tissue (RI) results for the different groups are given. The antibody response was assessed with two ELISAs with a detergent extract (solid symbols) and the recombinant ApxIIA protein (open symbols) as the solid-phase antigen. The response was quantified as the serum titer in comparison to an internal negative control (detergent extract ELISA) and in EU (based on an external standard) in the ApxIIA ELISA. For the standardized ApxIIA ELISA, activities of ≤10 EU in the sera are considered negative, 11 to 25 EU is intermediate, and >25 EU is a positive result. The central square within the hourglass shape represents the geometric mean, the hinges present the values in the middle of each half of data, and the top and bottom squares mark the maximum and minimum values, respectively. The asterisk denotes statistical significance (P < 0.05) for the lung lesion score (Wilcoxon test).