Abstract
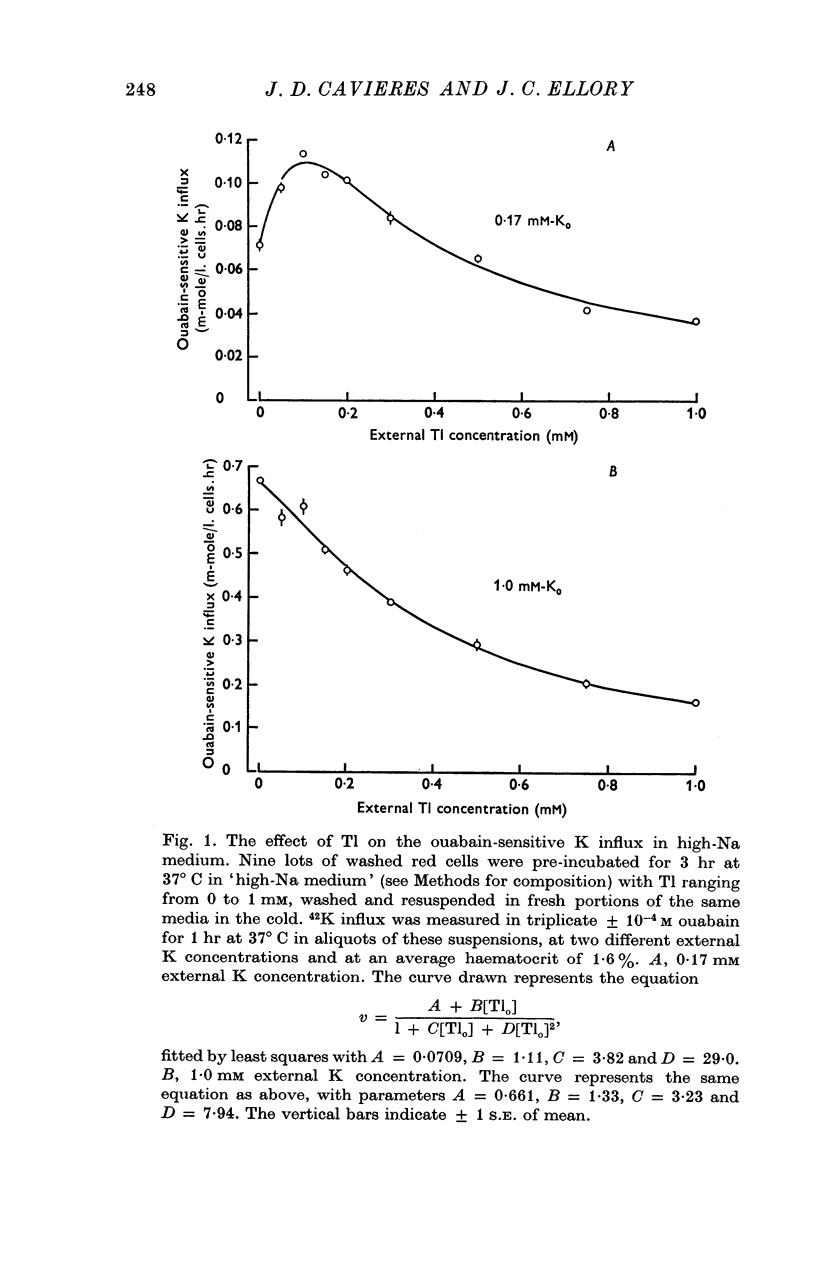
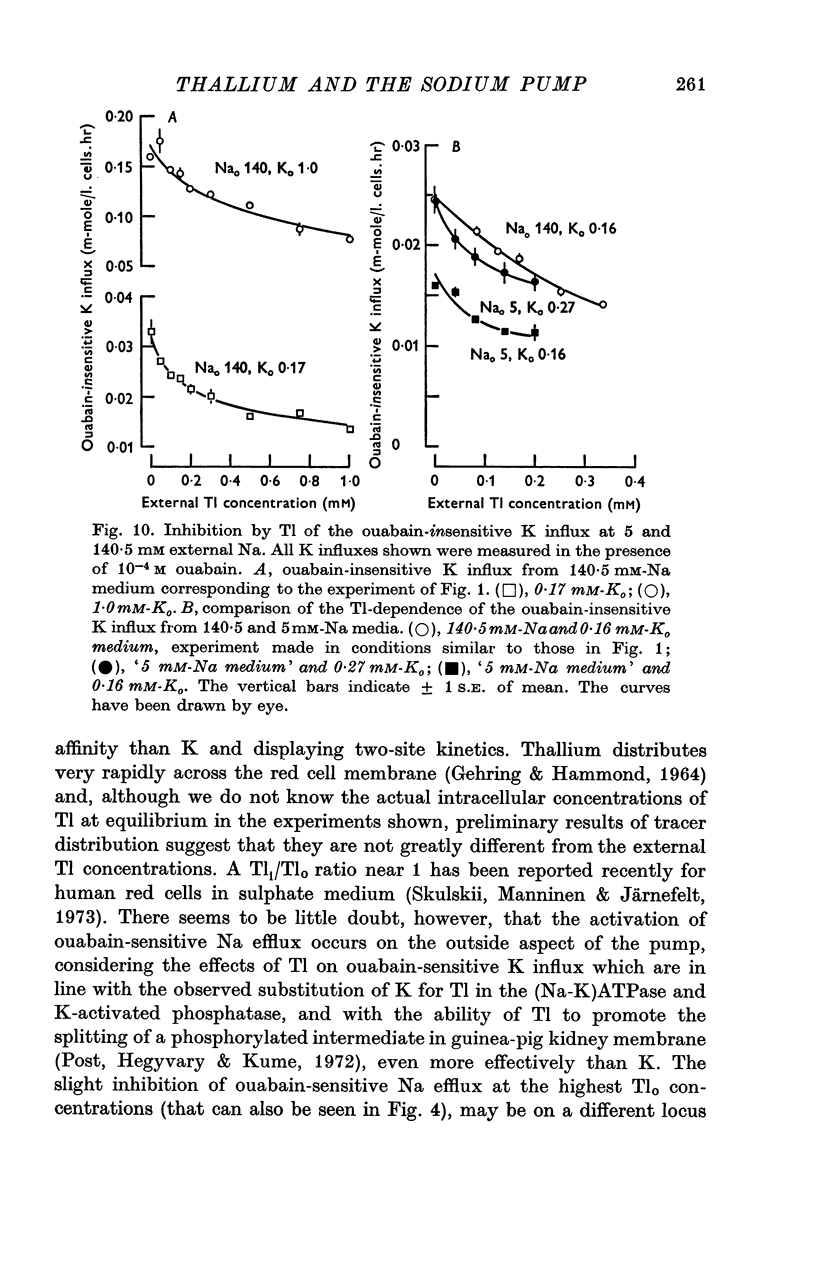
1. Thallium (Tl) inhibits the ouabain-sensitive K influx in human red cells in high-Na medium. At 1 mM external K concentration [Ko], the ouabain-sensitive K influx decreases steadily with increasing Tl concentration, up to 0·9 mM outside; at 0·17 mM-Ko, however, Tl stimulates the ouabain-sensitive K influx below 0·1 mM-Tlo and inhibits it at higher concentrations.
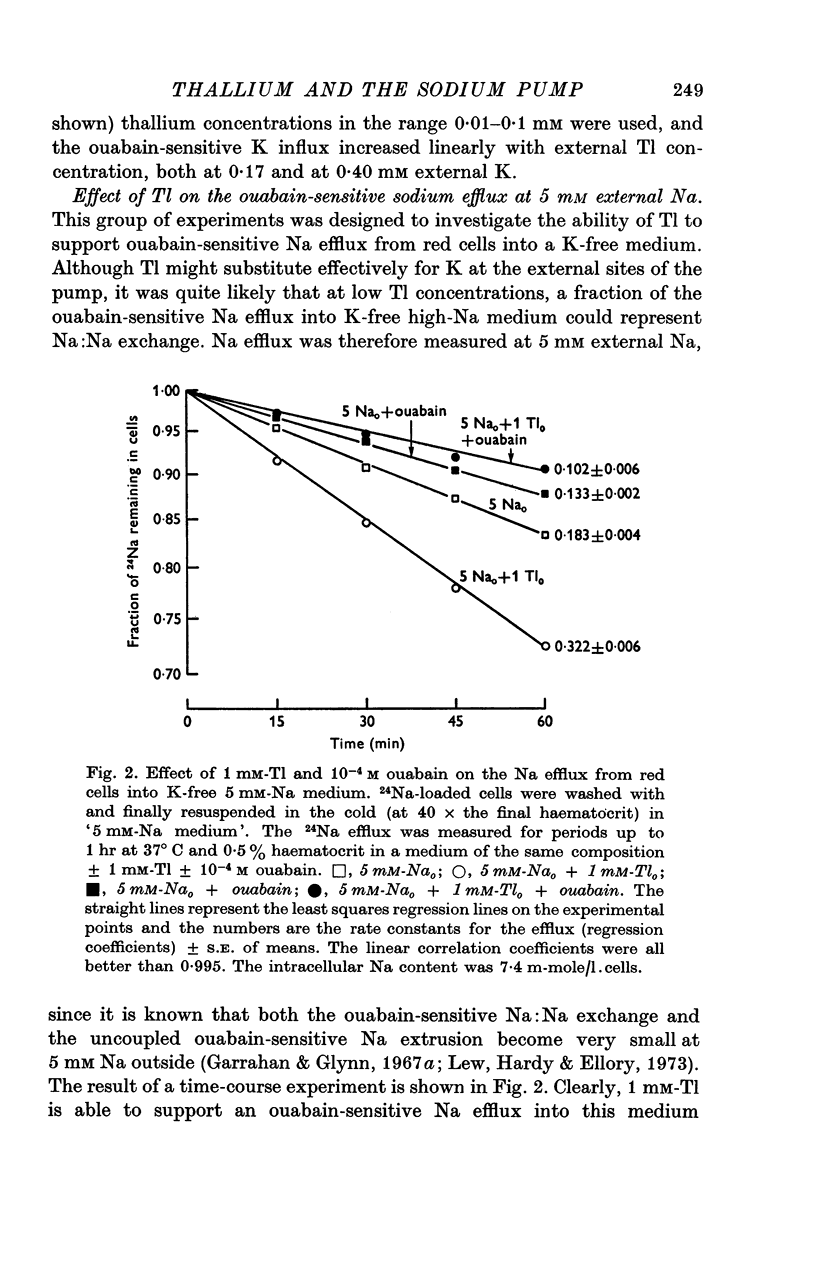
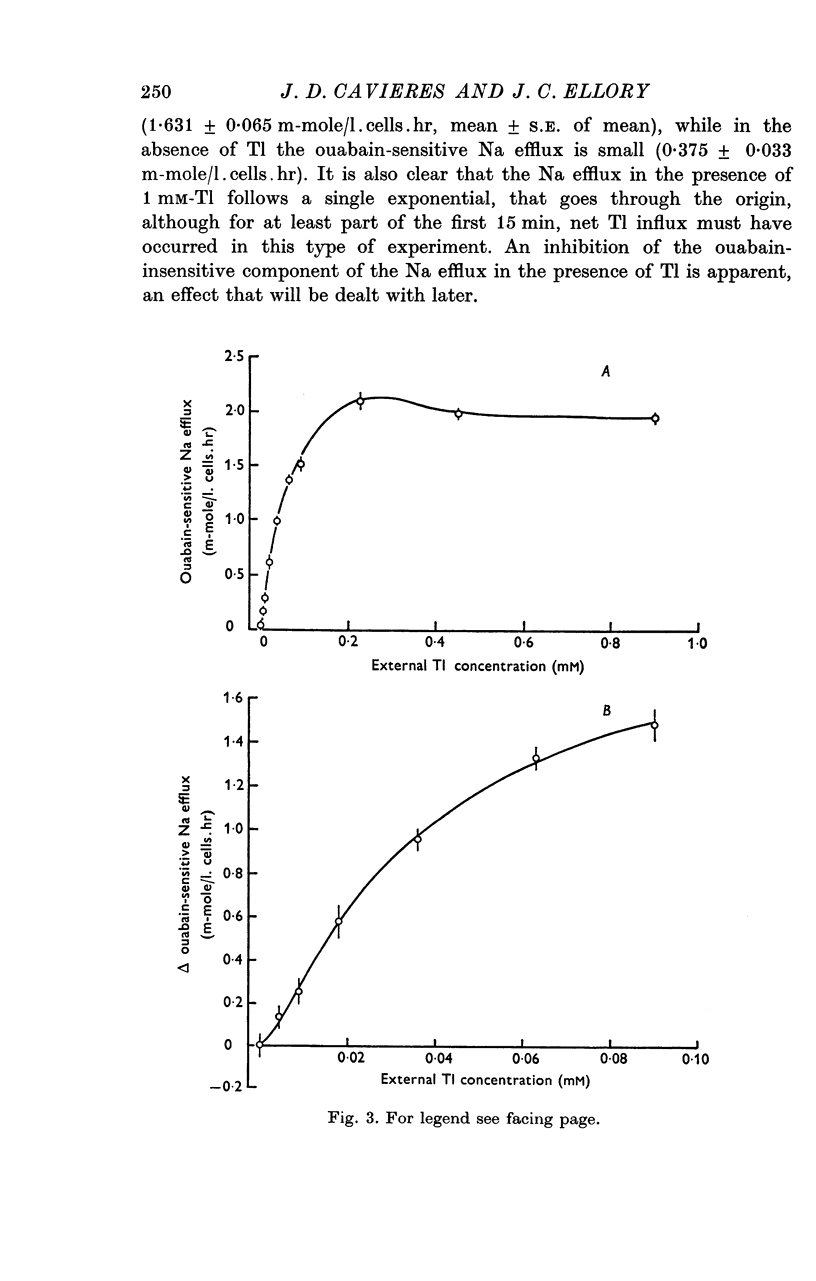
2. In a K-free medium in which all except 5 mM-Na is replaced by choline, and into which red cells show zero control ouabain-sensitive Na efflux, Tl is able to support ouabain-sensitive Na efflux up to 2·1 m-mole/l. cells.hr following a sigmoid activation curve which is half-maximal between 0·03 and 0·05 mM-Tlo and that follows two-site kinetics up to 0·1 mM-Tlo. Beyond 0·15 mM-Tlo, the Tl-activated ouabain-sensitive Na efflux attained is inhibited slightly.
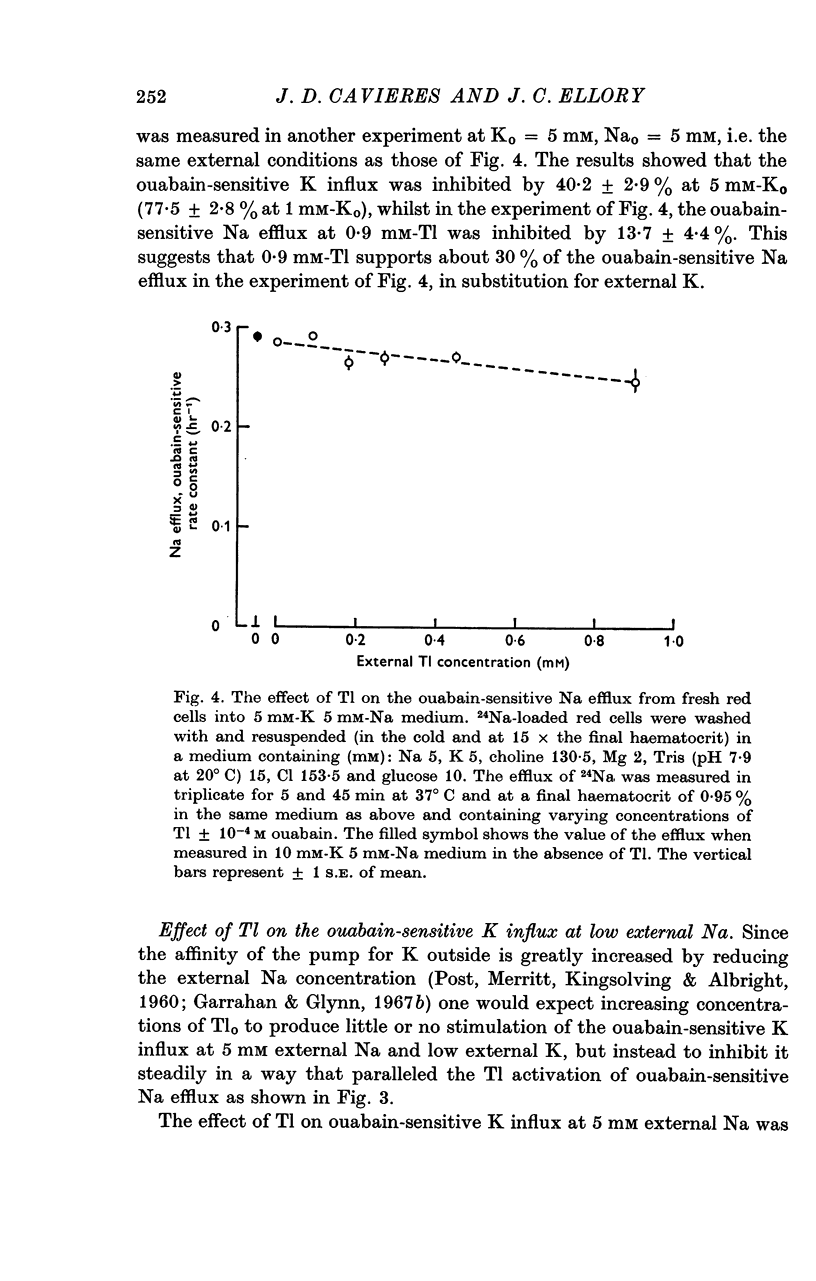
3. When the ouabain-sensitive Na efflux is measured at 5 mM-Nao and 5 mM-Ko, increasing concentrations of Tl have little effect on it, 0·9 mM-Tlo inhibiting by some 14%; in similar conditions, the ouabain-sensitive K influx is inhibited by about 40%.
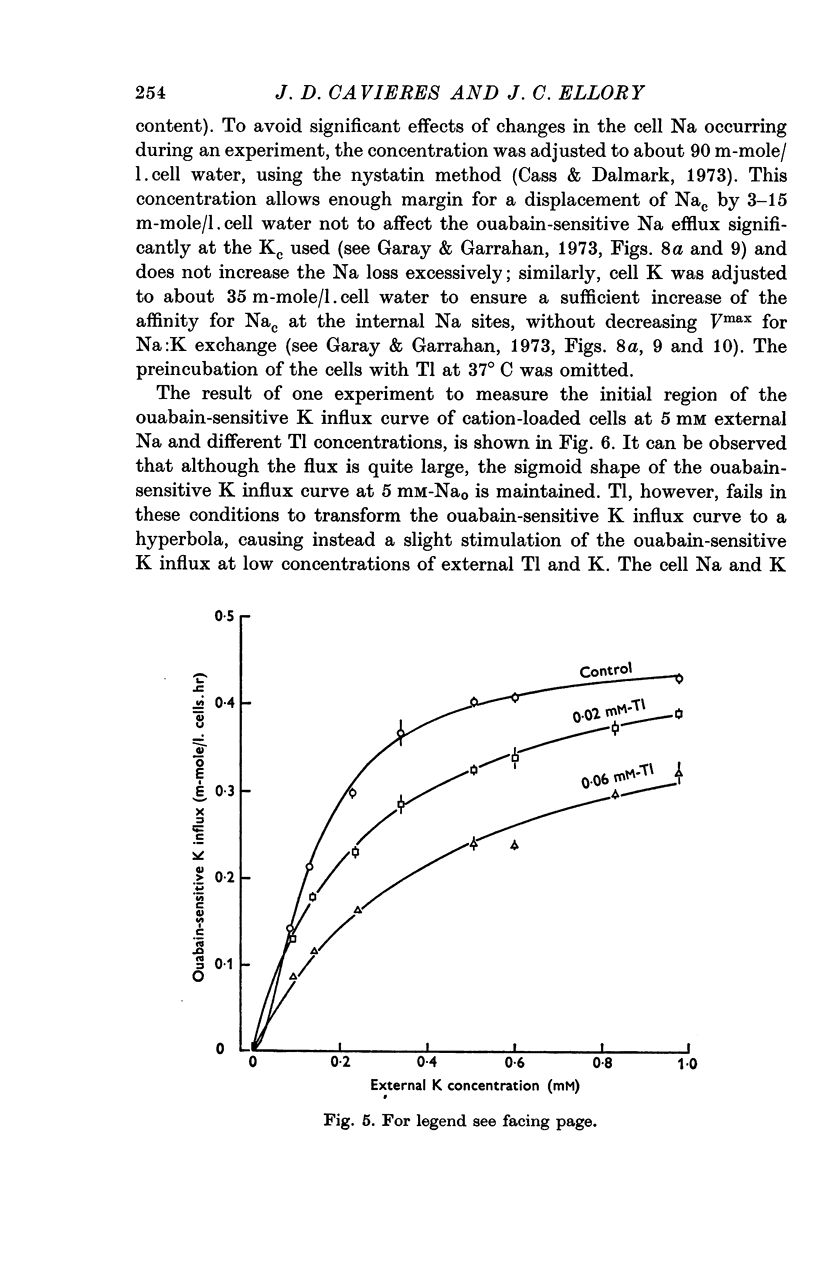
4. The dependence of ouabain-sensitive K influx on external K concentration at 5 mM-Nao, which follows a slightly sigmoid curve in the absence of Tl, changes to hyperbolic at 0·06 mM-Tlo at the same time that ouabain-sensitive K influx is inhibited. The fitted Vmax values for ouabain-sensitive K influx are the same in the presence and in the absence of 0·06 mM-Tlo.
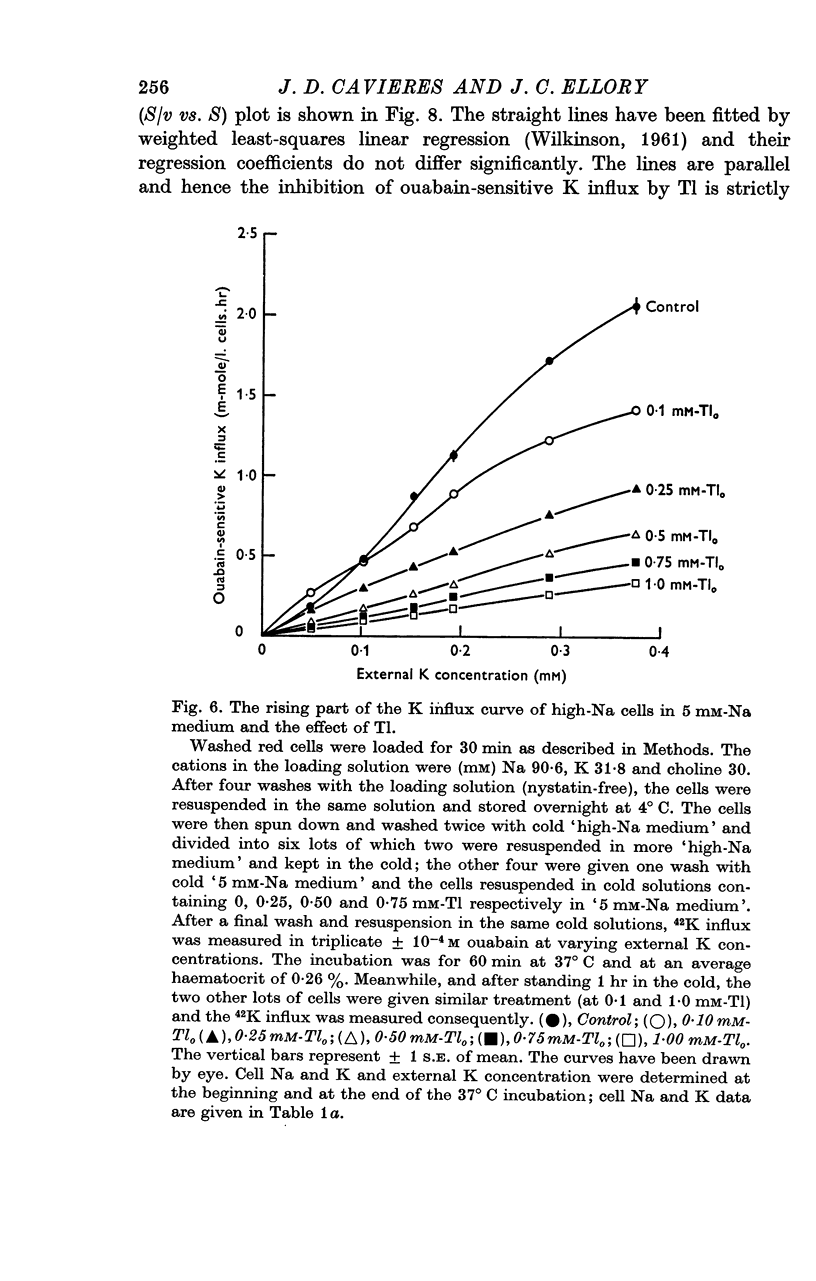
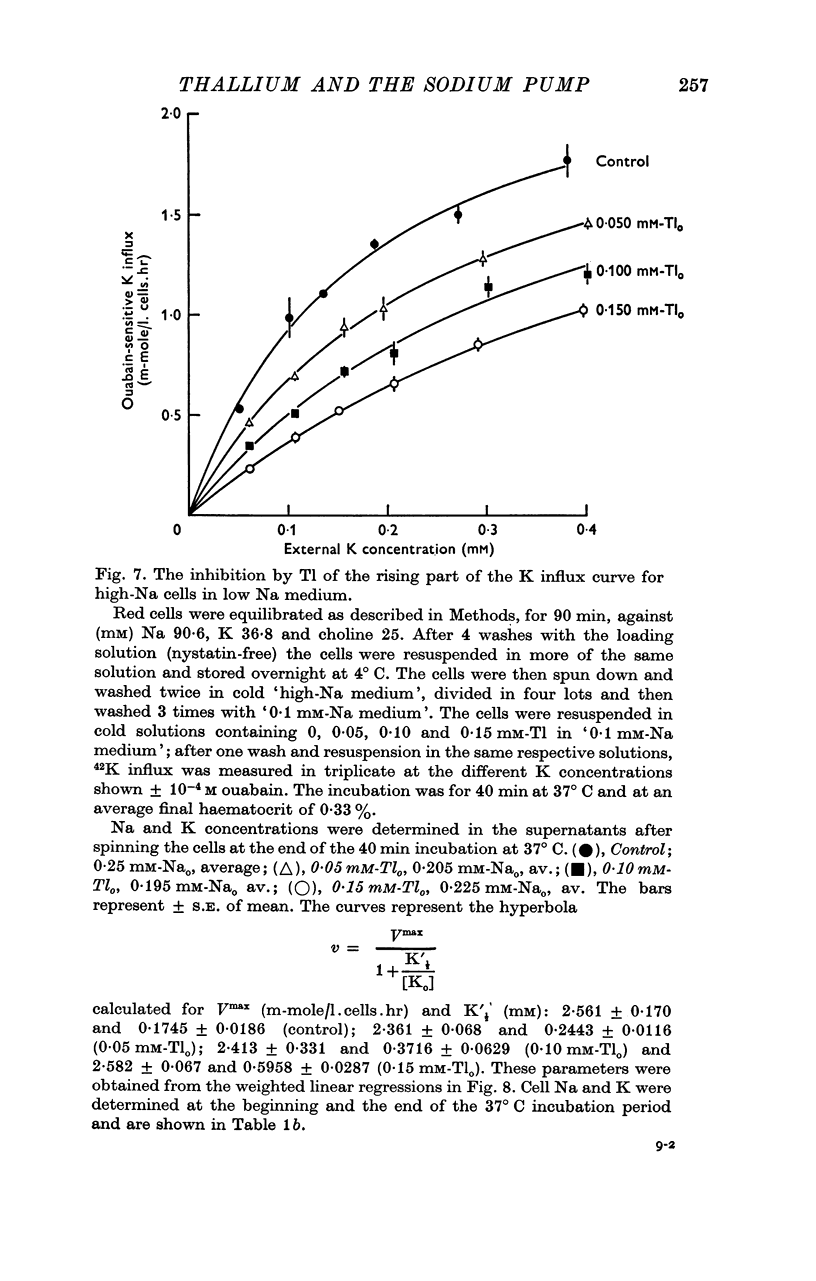
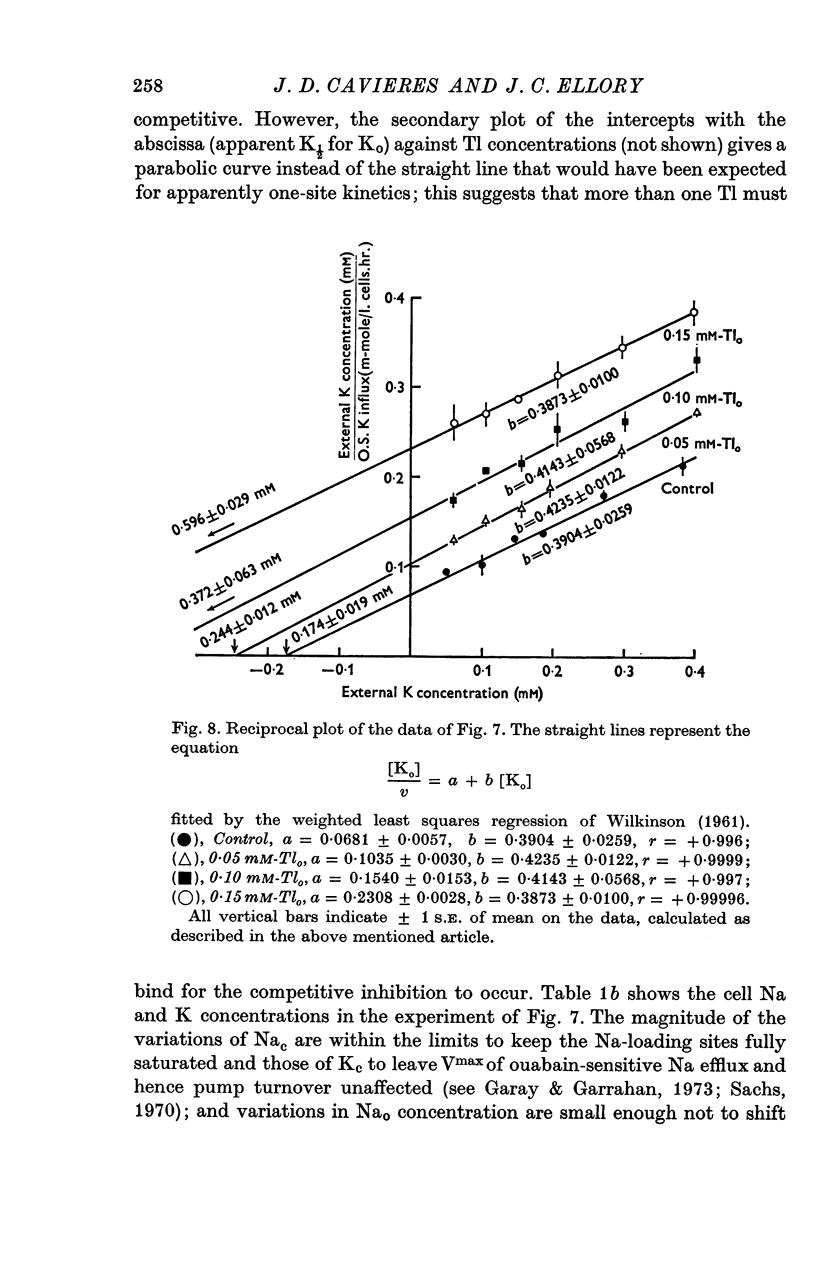
5. In high-Na cells, loaded by nystatin treatment, the ouabain-sensitive K influx measured at 0·2 mM-Nao follows a hyperbolic curve between 0·05 and 0·4 mM-Ko, and is inhibited by Tl in a strictly competitive fashion.
6. The effects of Tl on ouabain-sensitive Na efflux and ouabain-sensitive K influx are interpreted in terms of a high-affinity substitution for K at the external K sites of the Na pump and suggest that in human red cells Tl can be actively transported inwards in exchange for internal Na.
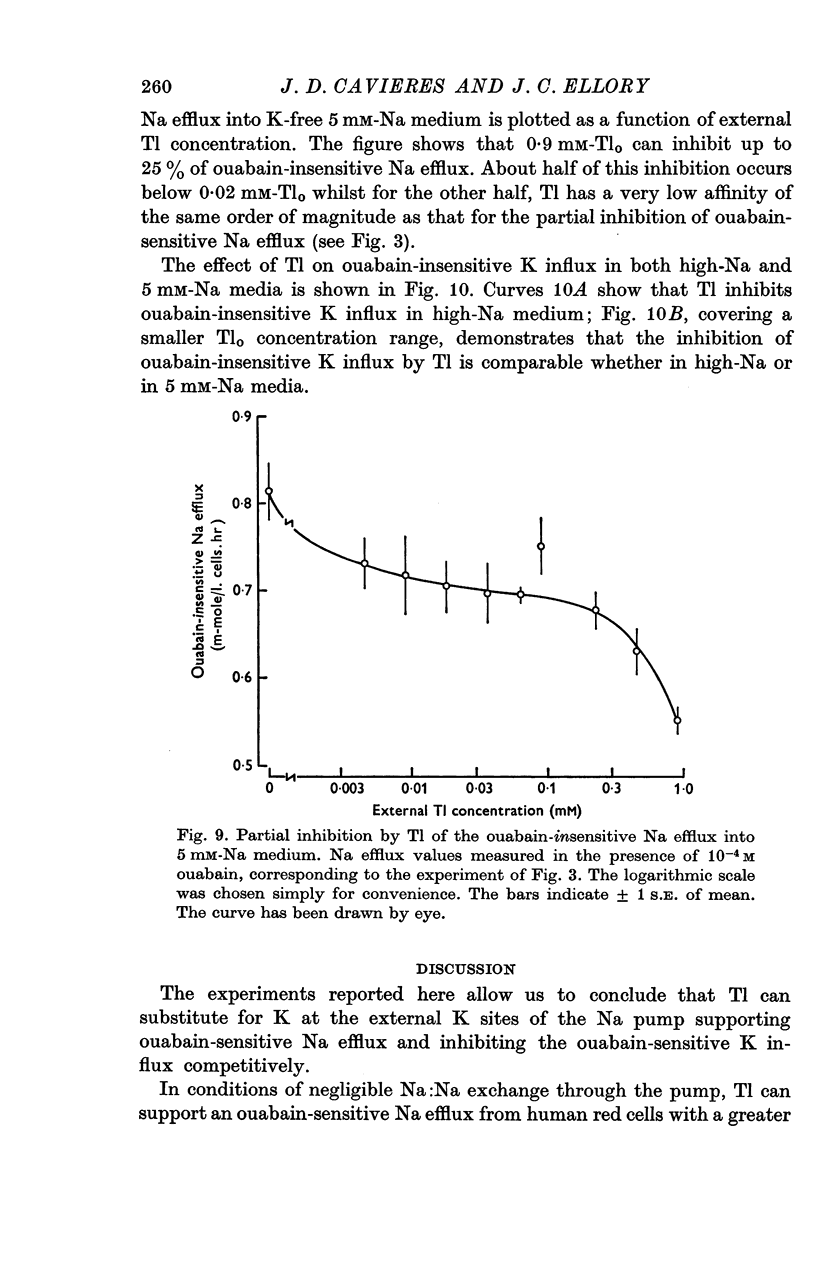
7. Thallium can inhibit about 25% of the ouabain-insensitive Na efflux into 5 mM-Nao and part of this inhibition occurs with a high Tl-affinity; the ouabain-insensitive K influx is inhibited by Tl both in high-Na and in 5 mM-Na medium, but with a different concentration dependence than the ouabain-insensitive Na efflux.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brading A. F., Jones A. W. Distribution and kinetics of CoEDTA in smooth muscle, and its use as an extracellular marker. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):387–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten J. S., Blank M. Thallium activation of the (Na+--K+)-activated ATPase of rabbit kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 24;159(1):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass A., Dalmark M. Equilibrium dialysis of ions in nystatin-treated red cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):47–49. doi: 10.1038/newbio244047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:581–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellory J. C., Nibelle J., Smith M. W. The effect of salt adaptation on the permeability and cation selectivity of the goldfish intestinal epithelium. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):105–115. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEHRING P. J., HAMMOND P. B. THE UPTAKE OF THALLIUM BY RABBIT ERYTHROCYTES. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Aug;145:215–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Garrahan P. J. The interaction of sodium and potassium with the sodium pump in red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):297–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. Facftors affecting the relative magnitudes of the sodium:potassium and sodium:sodium exchanges catalysed by the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):189–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The behaviour of the sodium pump in red cells in the absence of external potassium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):159–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The sensitivity of the sodium pump to external sodium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):175–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Lew V. L., Lüthi U. Reversal of the potassium entry mechanism in red cells, with and without reversal of the entire pump cycle. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):371–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Potassium channels in myelinated nerve. Selective permeability to small cations. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):669–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):637–658. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. F., Kregenow F. M. The characterization of new energy dependent cation transport processes in red blood cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):566–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. G., Tosteson D. C. Active sodium and potassium transport in high potassium and low potassium sheep red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):438–466. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inturrisi C. E. Thallium activation of K+-activated phosphatases from beef brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):567–569. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayne F. J. Thallium (I) activation of pyruvate kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Mar;143(1):232–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90204-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Hardy M. A., Jr, Ellory J. C. The uncoupled extrusion of Na+ through the Na+ pump. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):251–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., MERRITT C. R., KINSOLVING C. R., ALBRIGHT C. D. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potassium in the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1796–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Hegyvary C., Kume S. Activation by adenosine triphosphate in the phosphorylation kinetics of sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6530–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Competitive effects of some cations on active potassium transport in the human red blood cell. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1433–1441. doi: 10.1172/JCI105635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Ouabain-insensitive sodium movements in the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Mar;57(3):259–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Sodium movements in the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Sep;56(3):322–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R., Welt L. G. The concentration dependence of active potassium transport in the human red blood cell. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):65–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI105512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skulskii I. A., Manninen V., Järnefelt J. Interaction of thallous ions with the cation transport mechanism in erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 29;298(3):702–709. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


