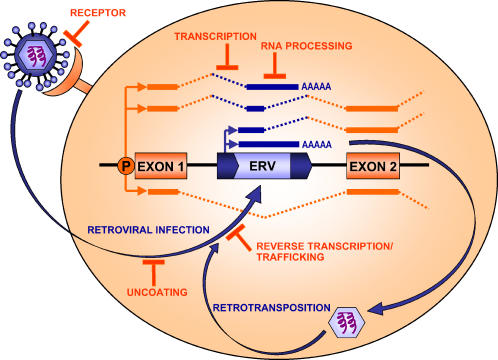
Figure 3. Host Restriction and Silencing of ERVs/LTRs.
Blocks to various stages of the retroviral or LTR retroelement life cycle are depicted as are silencing mechanisms affecting activity of integrated elements. Examples of restriction genes and silencing mechanisms: receptor block, Fv4; uncoating block, Trim5; reverse transcription/trafficking block, APOBEC3 and Fv1; transcription block, CpG methylation; and RNA processing block, Nxf1 and RNAi. See text and Table 2 for more details and other examples. An ERV or LTR element within an intron is shown to illustrate common gene-disruptive effects of such sequences through introduction of polyadenylation sites, promoters, and splice donor and acceptor sites. Spliced RNA is depicted with dashed lines. A normal gene transcript driven by the native promoter (P) is shown below the gene. A full-length retroviral transcript, which could be packaged for further rounds of retrotransposition or retroviral infection, is shown above the gene locus. Various potential aberrant or chimeric transcripts are shown above.