Abstract
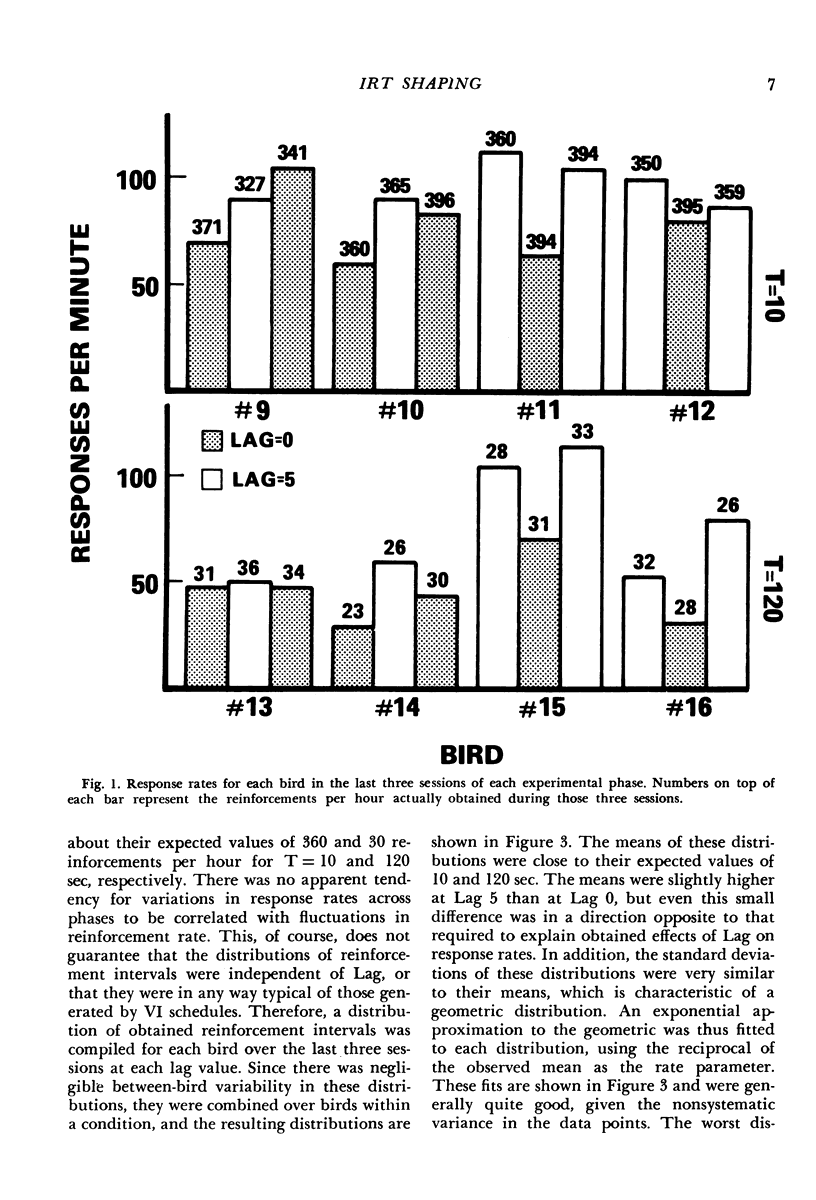
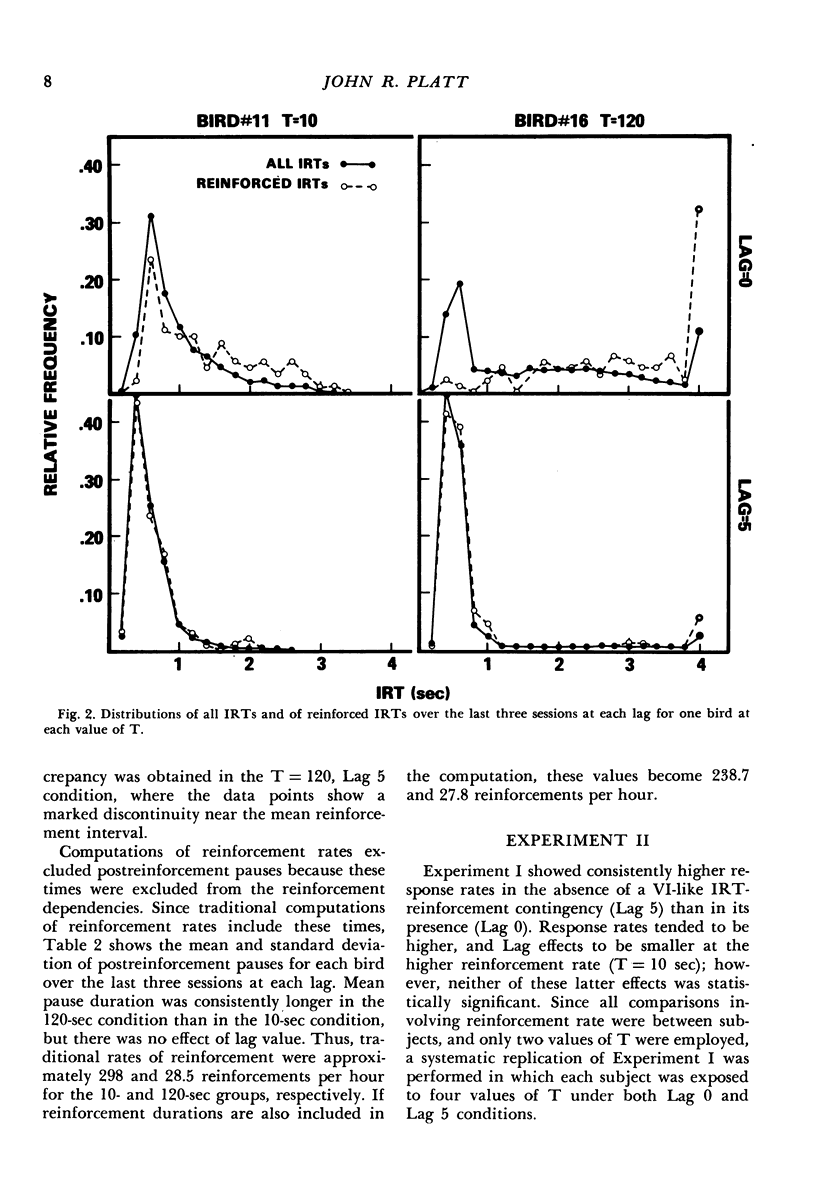
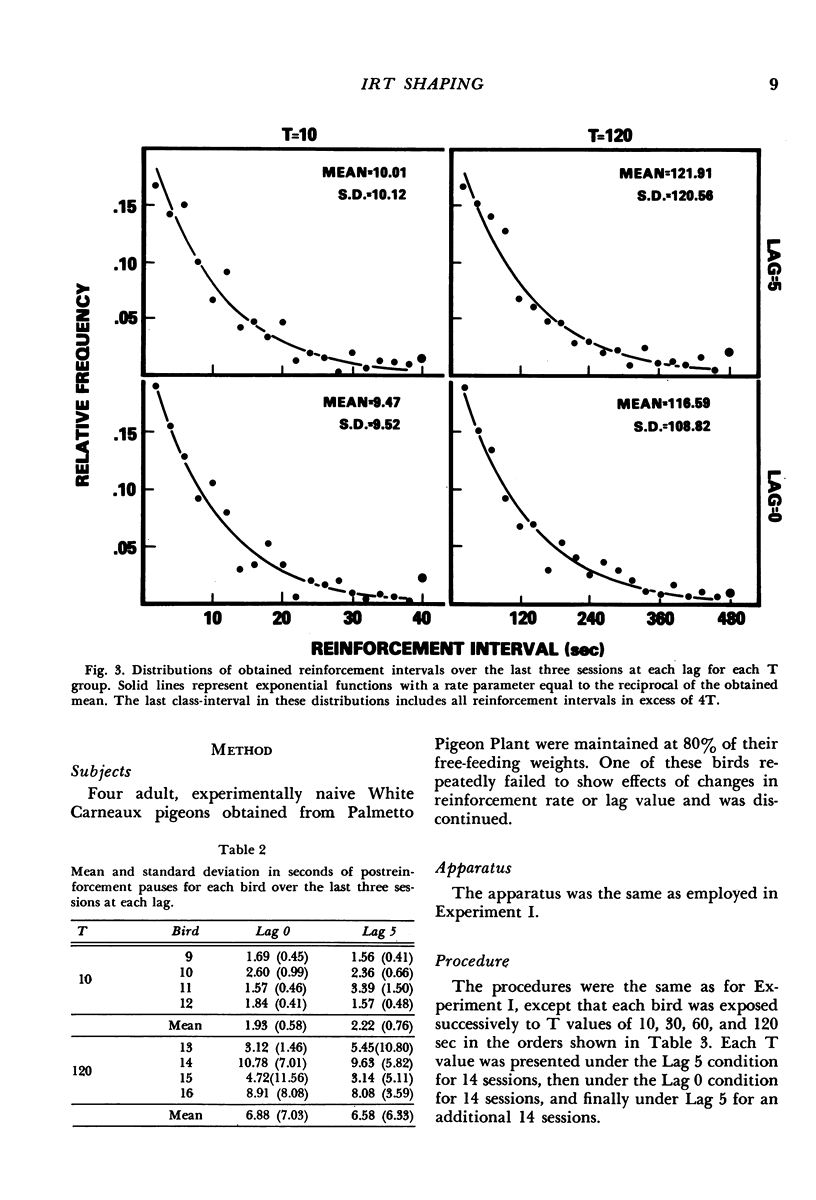
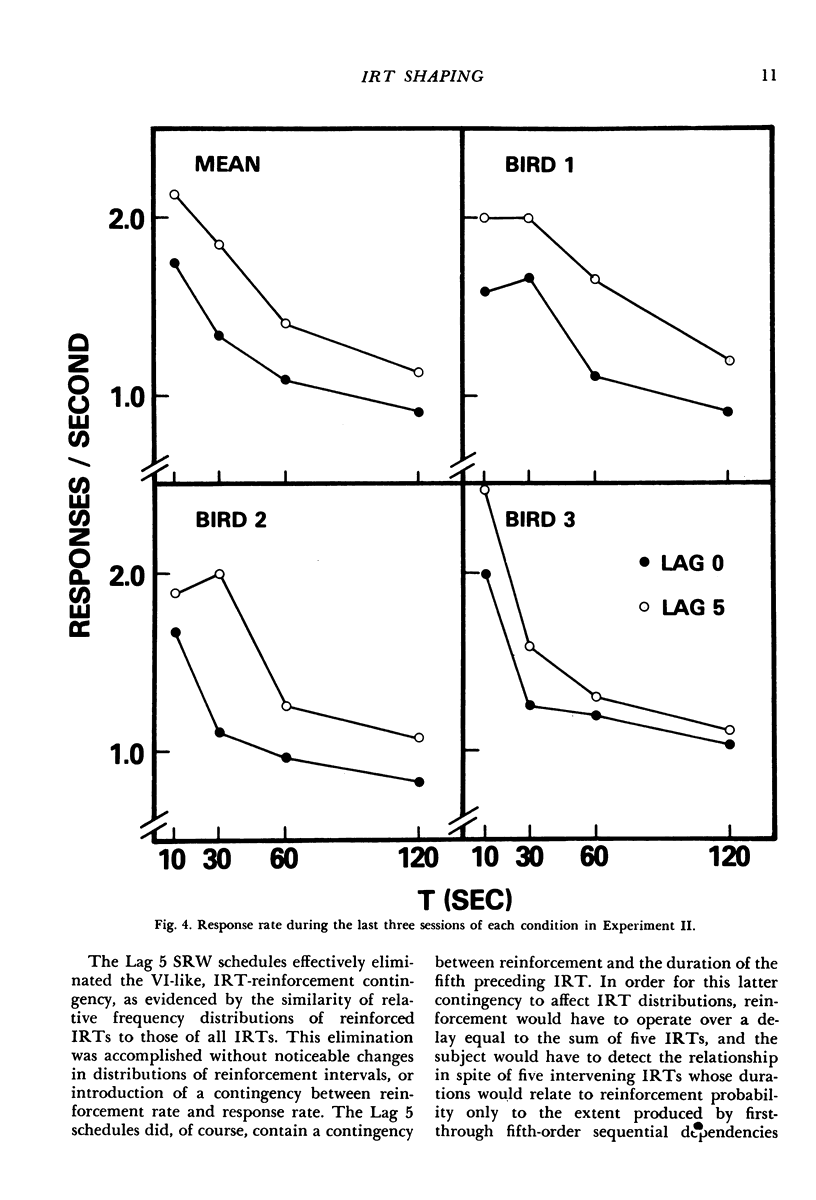
The interresponse-time reinforcement contingencies and distributions of interreinforcement intervals characteristic of certain variable-interval schedules were mimicked by reinforcing each key peck with a probability equal to the duration of the interresponse time it terminated, divided by the scheduled mean interreinforcement interval. The interresponse-time reinforcement contingency was then eliminated by basing the probability of reinforcement on the fifth interresponse time preceding the key peck. Even though distributions of interreinforcement intervals were unaffected by this manipulation, response rates consistently increased. A second experiment replicated this effect and showed it to combine additively with that of mean reinforcement rate. These results provide strong support for the contention that current analyses of variable-interval response rates that ignore the inherent interresponse-time reinforcement contingency may be seriously in error.
Keywords: IRT reinforcement, reinforcement rate, shaping, VI schedules, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGER D. The dependence of interresponse times upon the relative reinforcement of different interresponse times. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Sep;52(3):145–161. doi: 10.1037/h0041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anger D. The effect upon simple animal behavior of different frequencies of reinforcement, Part II: separate control of the reinforcement of different IRTs. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Sep;20(2):301–312. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. The correlation-based law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jul;20(1):137–153. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. L., Jenkins H. M. Auto-shaping of the pigeon's key-peck. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARMER J. PROPERTIES OF BEHAVIOR UNDER RANDOM INTERVAL REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:607–616. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuch D. O., Platt J. R. Reinforcement rate and interresponse time differentiation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Nov;26(3):471–486. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. K. A test of the effectiveness of the differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):385–391. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld W. N., Cumming W. W., Hearst E. ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Aug;42(8):563–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.8.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. Synthetic variable-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Mar;19(2):311–330. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. Time allocation and response rate. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):491–499. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


