Abstract
Six dairy cows (Bos taurus) were trained on several pairs of concurrent variable-interval schedules with different types of food available on each alternative. The required response was a plate press made by the animal's muzzle. Performance generally replicated that found with other species. The generalized matching law accounted for the preference data, showing that food preference could be quantitatively analyzed as a special case of response bias. The preference functions showed that the response- and time-allocation ratios were not as extreme as obtained reinforcement rate ratios (undermatching).
Keywords: different reinforcers, concurrent schedules, matching law, nose-plate press, cows
Full text
PDF


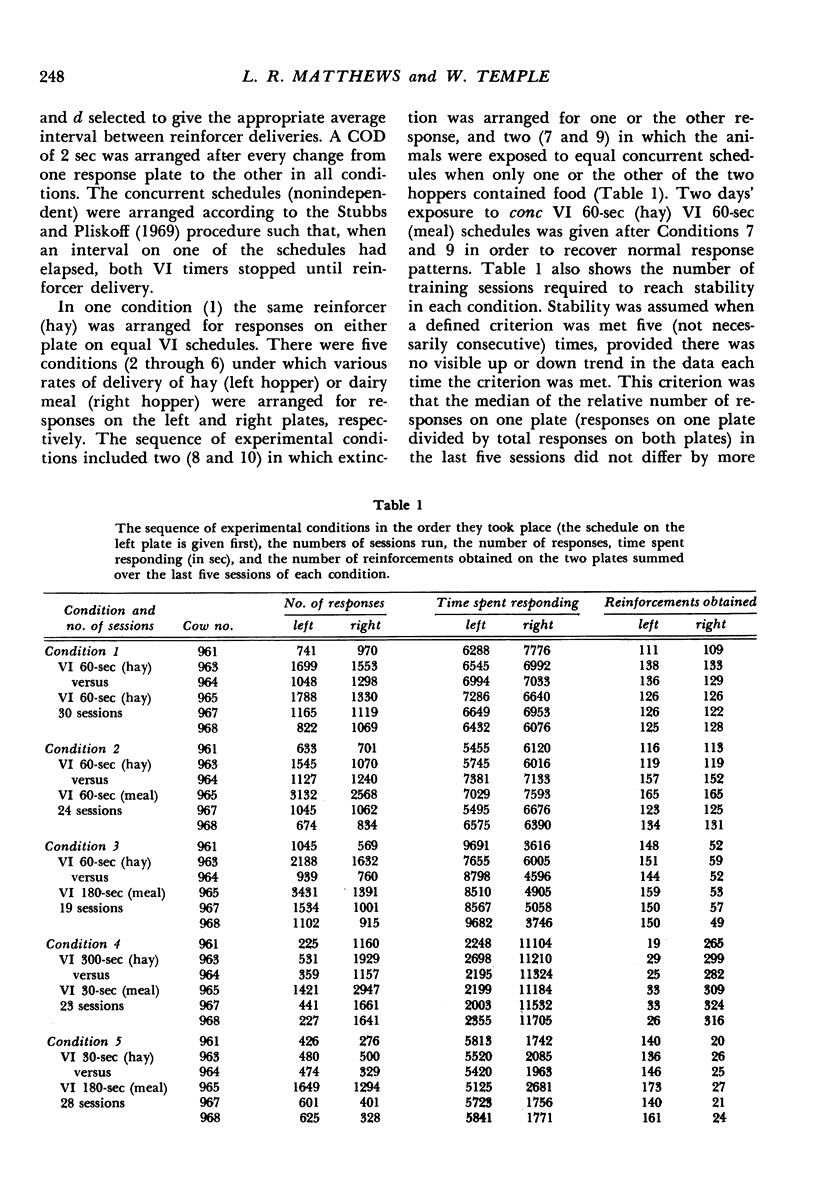
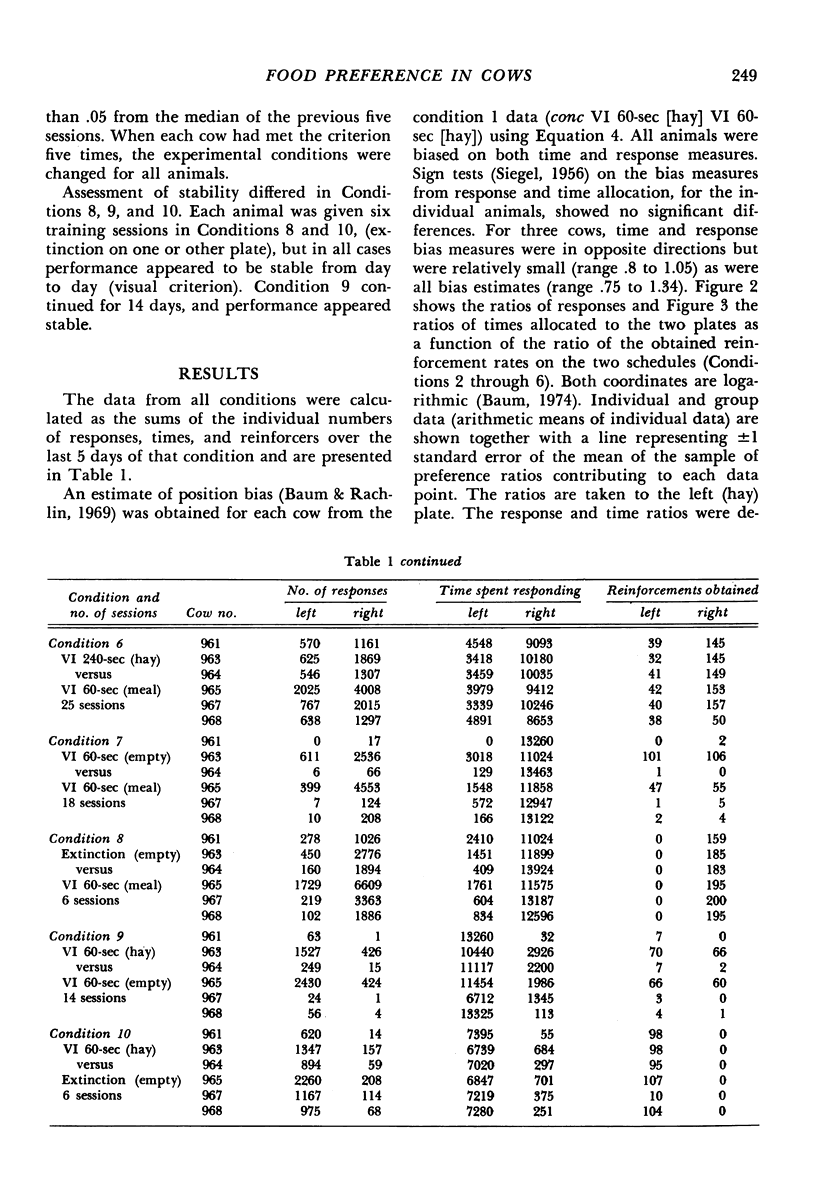
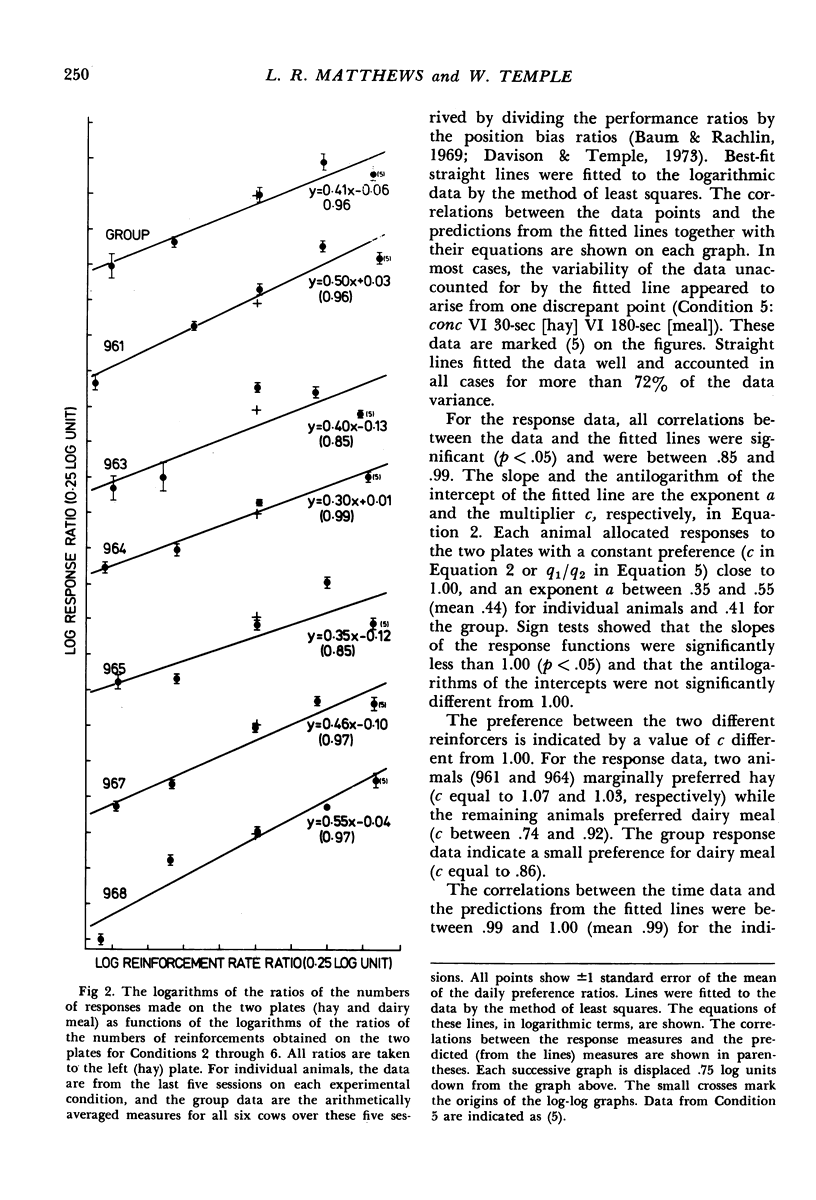
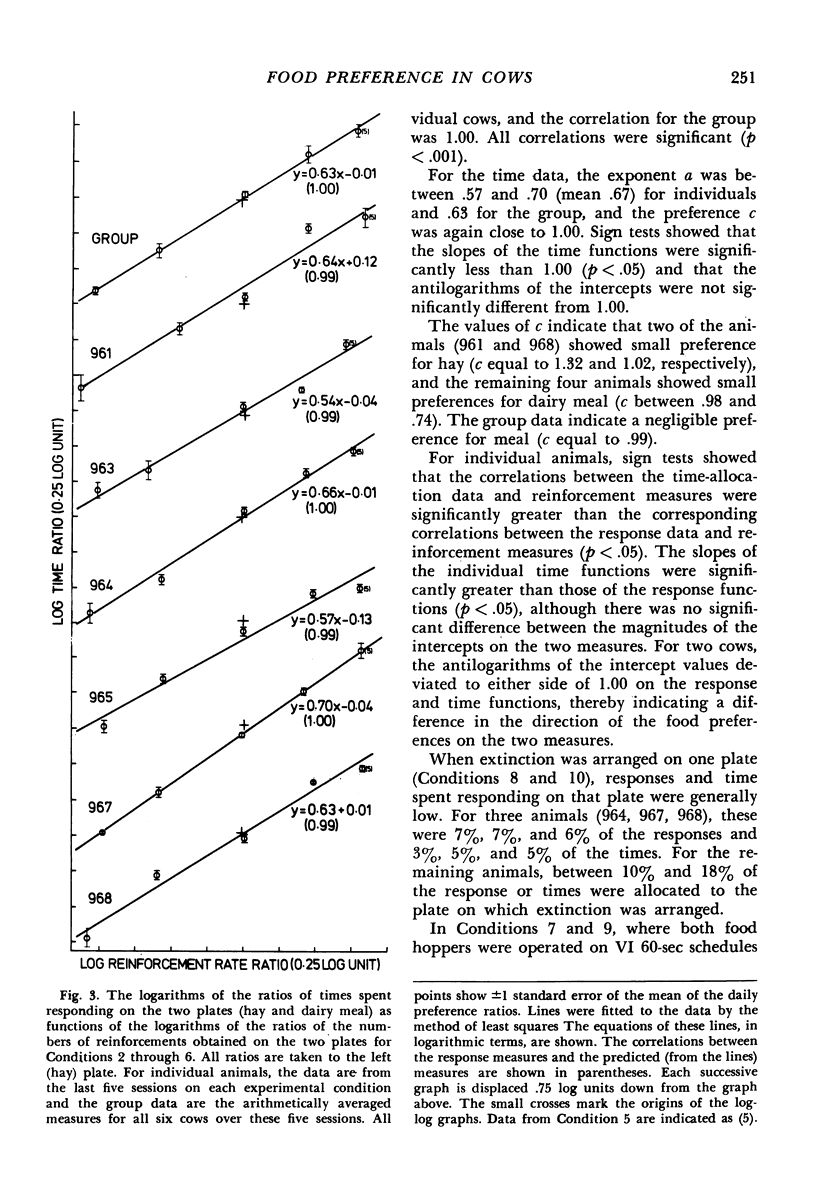



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. On two types of deviation from the matching law: bias and undermatching. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):231–242. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M., Rachlin H. C. Choice as time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):861–874. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C., Hunter I. W. Performance on variable-interval schedules arranged singly and concurrently. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 May;25(3):335–345. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C., Temple W. Preference for fixed-interval schedules: an alternative model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):393–403. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollard V., Davison M. C. Preference for qualitatively different reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):375–380. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. The matching law. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):489–495. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb B., Davison M. C. Performance in concurrent interval schedules: a systematic replication. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Sep;24(2):191–197. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. L. Matching-based hedonic scaling in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Nov;26(3):335–347. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. L., Pliskoff S. S. Changeover delay and concurrent schedules: some effects on relative performance measures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Nov;10(6):517–527. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A., Pliskoff S. S. Concurrent responding with fixed relative rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):887–895. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]