Abstract
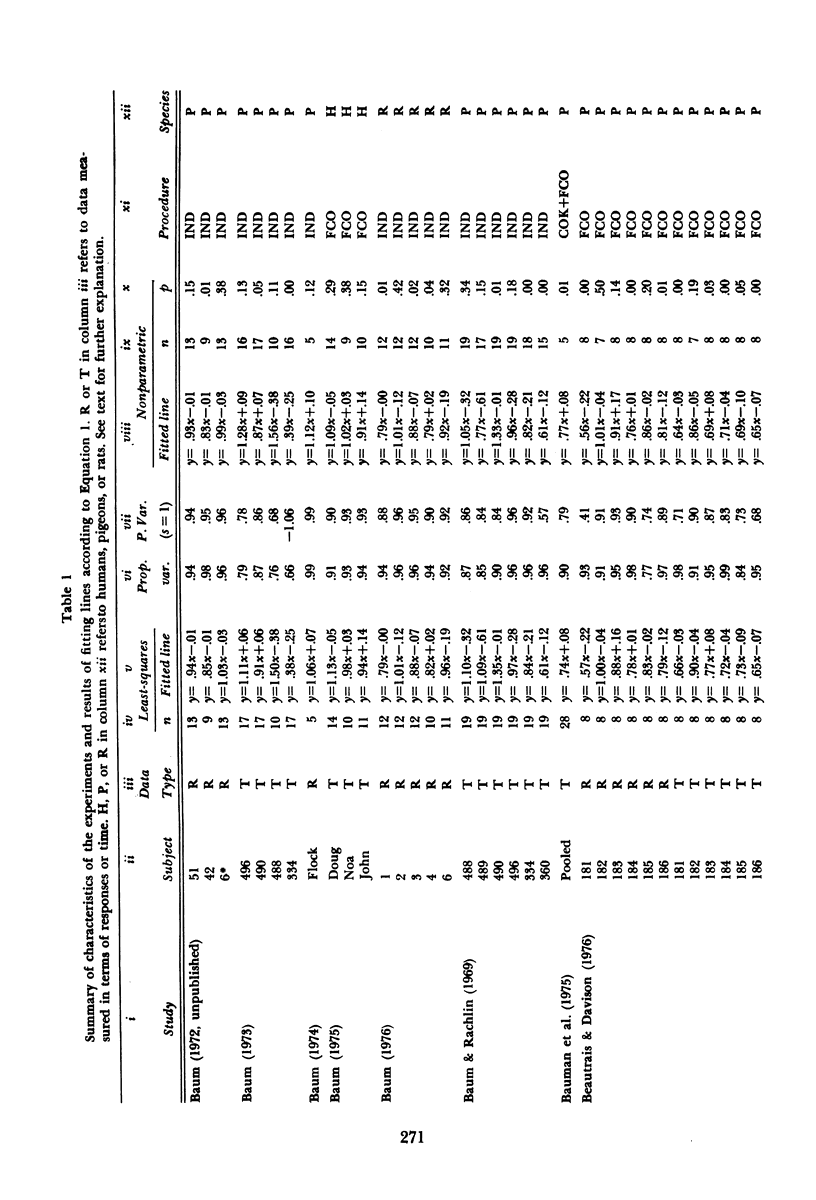
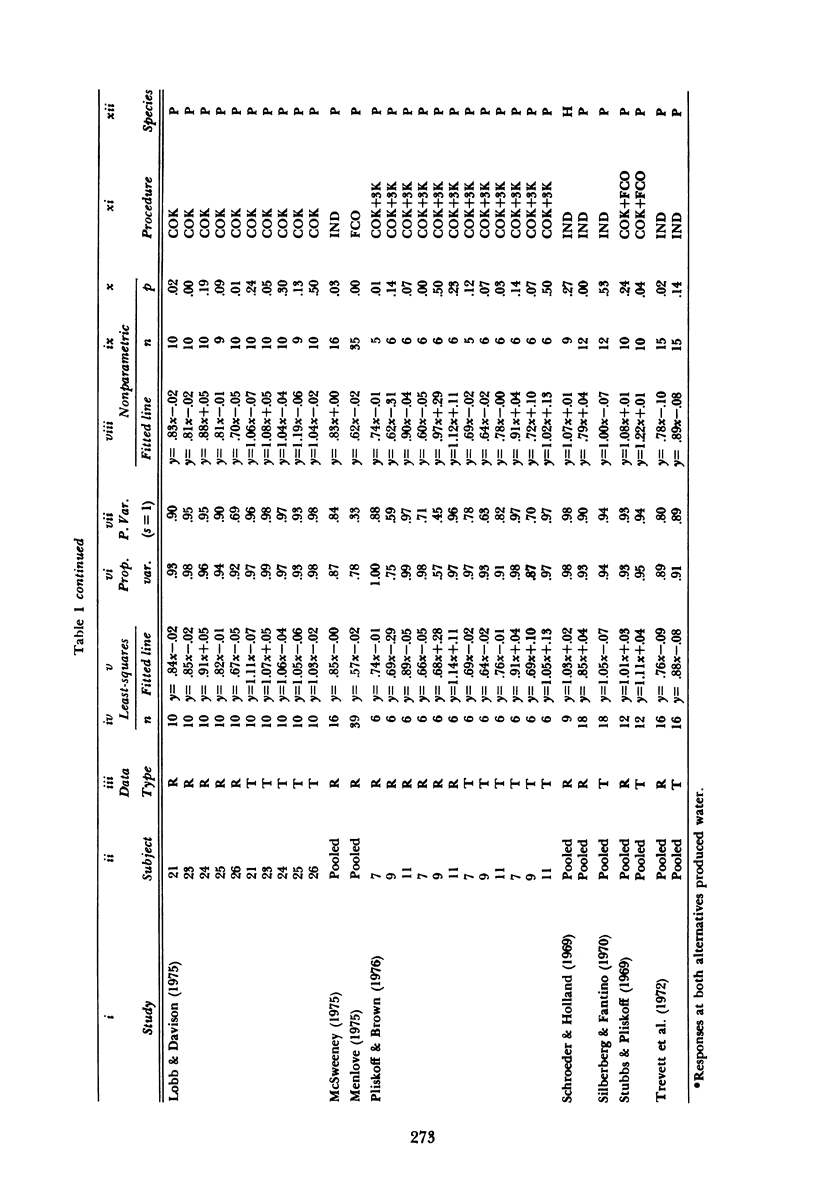
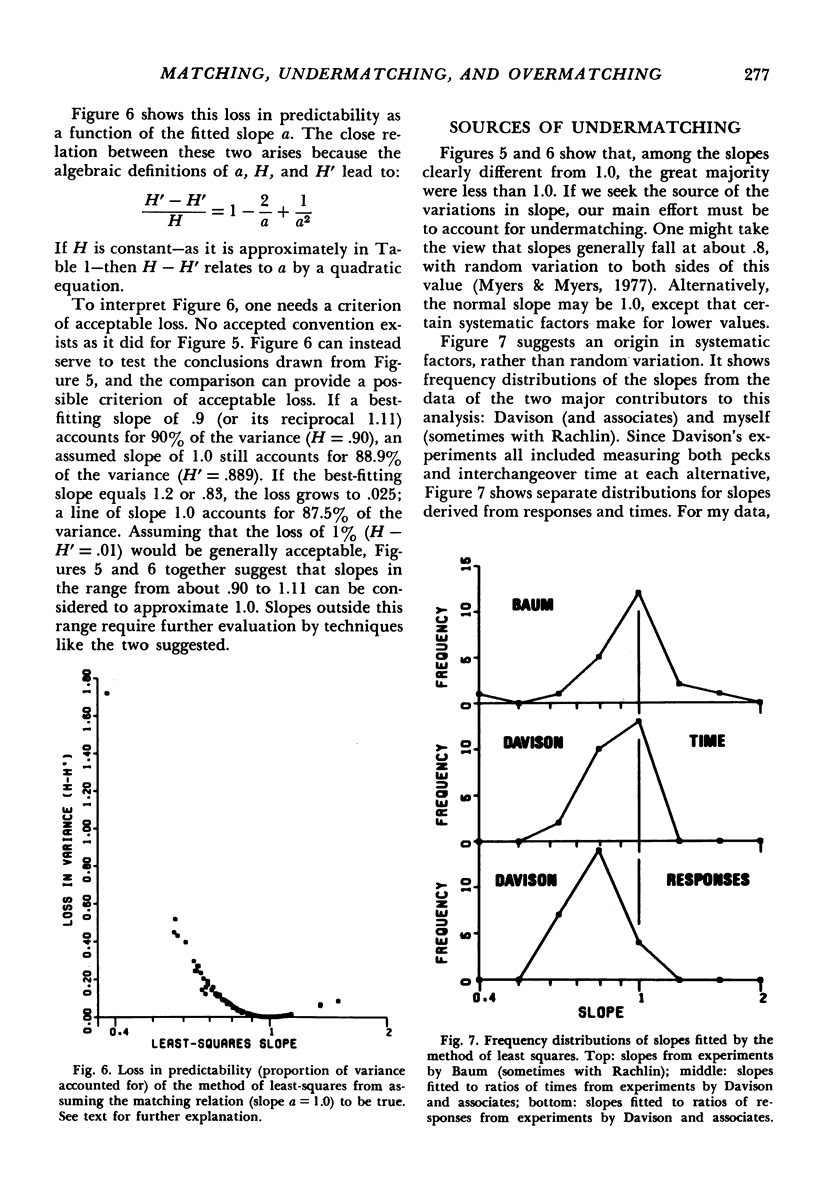
Almost all of 103 sets of data from 23 different studies of choice conformed closely to the equation: log (B1/B2) = a log (r1/r2) + log b, where B1 and B2 are either numbers of responses or times spent at Alternatives 1 and 2, r1 and r2 are the rates of reinforcement obtained from Alternatives 1 and 2, and a and b are empirical constants. Although the matching relation requires the slope a to equal 1.0, the best-fitting values of a frequently deviated from this. For B1 and B2 measured as numbers of responses, a tended to fall short of 1.0 (undermatching). For B1 and B2 measured as times, a fell to both sides of 1.0, with the largest mode at about 1.0. Those experiments that produced values of a for both responses and time revealed only a rough correspondence between the two values; a was often noticeably larger for time. Statistical techniques for assessing significance of a deviation of a from 1.0 suggested that values of a between .90 and 1.11 can be considered good approximations to matching. Of the two experimenters who contributed the most data, one generally found undermatching, while the other generally found matching. The difference in results probably arises from differences in procedure. The procedural variations that lead to undermatching appear to be those that produce (a) asymmetrical pausing that favors the poorer alternative; (b) systematic temporal variation in preference that favors the poorer alternative; and (c) patterns of responding that involve changing over between alternatives or brief bouts at the alternatives.
Keywords: matching relation, undermatching, overmatching, choice, conc VIVI
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. Chained concurrent schedules: reinforcement as situation transition. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):91–101. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. Choice in free-ranging wild pigeons. Science. 1974 Jul 5;185(4145):78–79. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4145.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. On two types of deviation from the matching law: bias and undermatching. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):231–242. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M., Rachlin H. C. Choice as time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):861–874. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. Time allocation in human vigilance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jan;23(1):45–53. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. Time-based and count-based measurement of preference. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Jul;26(1):27–35. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman R. A., Shull R. L., Brownstein A. J. Time allocation on concurrent schedules with asymmetrical response requirements. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jul;24(1):53–57. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beautrais P. G., Davison M. C. Response and time allocation in concurrent second-order schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jan;27(1):61–69. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein A. J., Pliskoff S. S. Some effects of relative reinforcement rate and changeover delay in response-independent concurrent schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):683–688. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Independence of concurrent responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:175–184. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C., Hunter I. W. Performance on variable-interval schedules arranged singly and concurrently. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 May;25(3):335–345. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deluty M. Z., Church R. M. Time-allocation matching between punishing situations. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Mar;29(2):191–198. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Squires N., Delbrück N., Peterson C. Choice behavior and the accessibility of the reinforcer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):35–43. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findley J. D. Preference and Switching under Concurrent Scheduling. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):123–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graft D. A., Lea S. E., Whitworth T. L. The matching law in and within groups of rats. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jan;27(1):183–194. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollard V., Davison M. C. Preference for qualitatively different reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):375–380. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh S. R. The economics of daily consumption controlling food- and water-reinforced responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 May;29(3):475–491. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. Preference for fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Sep;14(2):127–131. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb B., Davison M. C. Performance in concurrent interval schedules: a systematic replication. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Sep;24(2):191–197. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland D. J., Sibly R. M. The behavioural final common path. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 May 15;270(907):265–293. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menlove R. L. Local patterns of responding maintained by concurrent and multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 May;23(3):309–337. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menlove R. L., Moffitt M., Shimp C. P. Choice between concurrent schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Mar;19(2):331–344. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. L. Matching-based hedonic scaling in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Nov;26(3):335–347. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers D. L., Myers L. E. Undermatching: a reappraisal of performance on concurrent variable-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jan;27(1):203–214. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Rates and patterns of responding with concurrent fixed-interval and variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Sep;16(2):241–247. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pliskoff S. S., Brown T. G. Matching with a trio of concurrent variable-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Jan;25(1):69–73. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pliskoff S. S. Effects of symmetrical and asymmetrical changeover delays on concurrent performances. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Sep;16(2):249–256. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENS S. S. On the psychophysical law. Psychol Rev. 1957 May;64(3):153–181. doi: 10.1037/h0046162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. A. A two-state analysis of fixed-interval responding in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):677–687. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder S. R., Holland J. G. Reinforcement of eye movement with concurrent schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):897–903. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. L., Pliskoff S. S. Changeover delay and concurrent schedules: some effects on relative performance measures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Nov;10(6):517–527. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg A., Fantino E. Choice, rate of reinforcement, and the changeover delay. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):187–197. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A., Pliskoff S. S. Concurrent responding with fixed relative rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):887–895. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevett A. J., Davison M. C., Williams R. J. Performance in concurrent interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):369–374. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


