Abstract
Experiment 1 investigated whether training subjects to read words aloud would induce correct written spelling of the words even though spelling had no experimental consequences. Training in reading was followed by a weak increment in correct spelling. Experiment 2 investigated whether overtraining in reading would improve spelling more. Spelling improved as overtraining continued until the subjects spelled all the words correctly. Experiments 3 and 4 investigated the components of overtraining responsible for this improvement in spelling. Initial training in reading followed by repeated opportunities to look at (but not say aloud) the printed words resulted in the same gradual improvement in spelling as seen in Experiment 2. The results were related to Skinner's theory of verbal behavior and to studies of the relationship between speaking and instruction-following in children.
Keywords: verbal behavior, reading, spelling, children
Full text
PDF


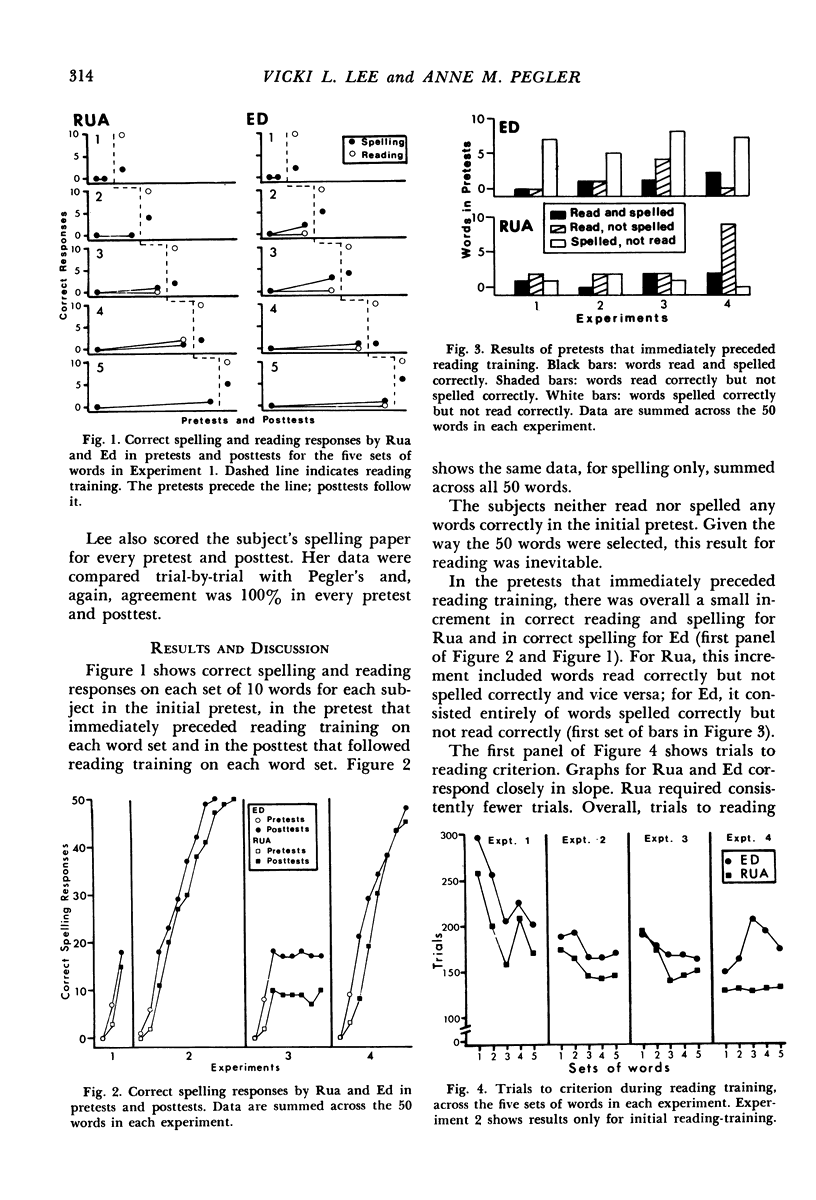
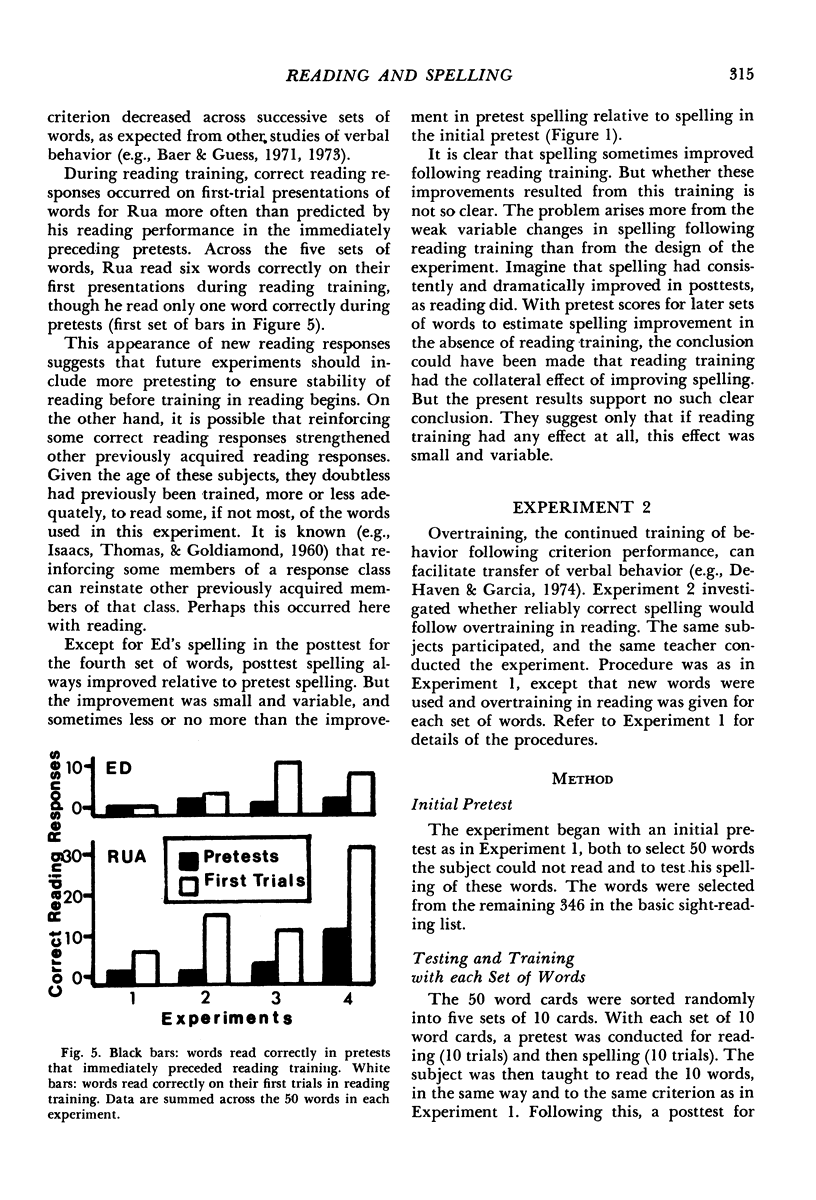







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer D. M., Guess D. Receptive training of adjectival inflections in mental retardates. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Summer;4(2):129–139. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer D. M., Guess D. Teaching productive noun suffixes to severely retarded children. Am J Ment Defic. 1973 Mar;77(5):498–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHaven E. D., Garcia E. E. Continuation of training as a variable influencing the generalization of speech in a retarded child. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1974 Sep;2(3):217–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00918889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guess D. A functional analysis of receptive language and productive speech: acquisition of the plural morpheme. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Spring;2(1):55–64. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guess D., Baer D. M. An analysis of individual differences in generalization between receptive and productive language in retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Summer;6(2):311–329. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS W., THOMAS J., GOLDIAMOND I. Application of operant conditioning to reinstate verbal behavior in psychotics. J Speech Hear Disord. 1960 Feb;25:8–12. doi: 10.1044/jshd.2501.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. L. Prepositional phrases spoken and heard. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Mar;35(2):227–242. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. A. The control of imitative and nonimitative behaviors in severely retarded children through "generalized-instruction following". J Exp Child Psychol. 1971 Jun;11(3):390–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(71)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. A., Shimoff E., Catania A. C., Sagvolden T. Uninstructed human responding: sensitivity to ratio and interval contingencies. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 May;27(3):453–467. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordquist V. M. The modification of a child's enuresis: some response-response relationships. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Fall;4(3):241–247. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahler R. G., Sperling K. A., Thomas M. R., Teeter N. C., Luper H. L. The modification of childhood stuttering: some response-response relationships. J Exp Child Psychol. 1970 Jun;9(3):411–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(70)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


