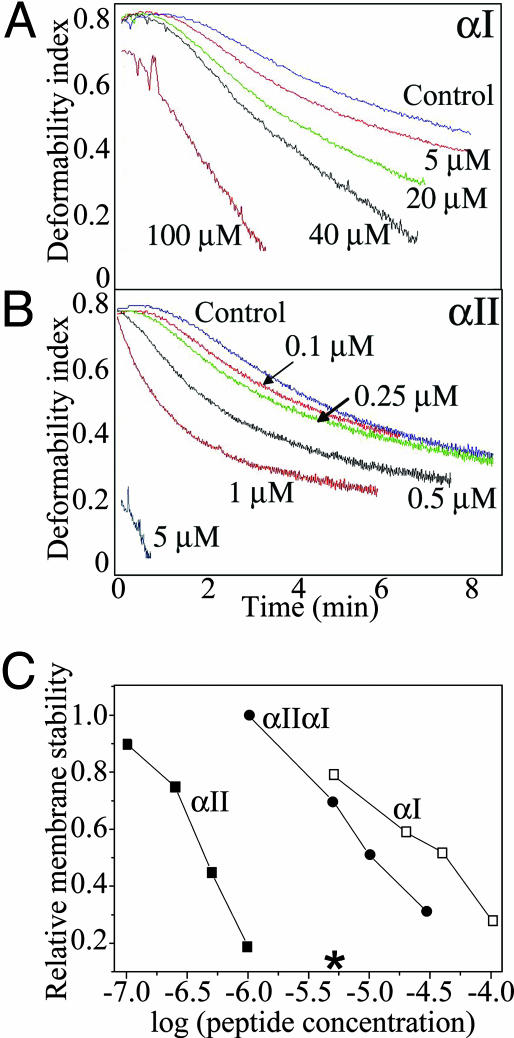
Fig. 6.
Effect of peptide incorporation on membrane stability. Membrane mechanical stability of the resealed ghosts was measured by ektacytometry. Membrane stability is expressed in terms of the rate of decline in deformability index (DI). Faster decay (DI curve shifted to the left) reflects destabilization of the membrane. A and B show the effects of incorporation of the αI and αII peptides, respectively; (C) correlation between relative membrane stability (the time taken to reach 50% loss of deformability) and peptide concentrations; open squares, αI; filled squares, αII; filled circles, αIIαI. *, A concentration of αII peptide that caused essentially instantaneous fragmentation.