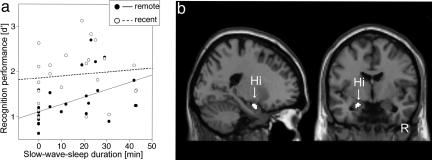
Fig. 2.
Behavioral and fMRI results: sleep effect. (a) Scatter plot of recognition memory performance (d′) on day 1 for recent and remote items related to individual slow-wave sleep duration. (b) A correlation based on weaker responses to confident remote hits as compared to confident recent hits with longer slow-wave sleep duration was observed in the left hippocampus (Hi).