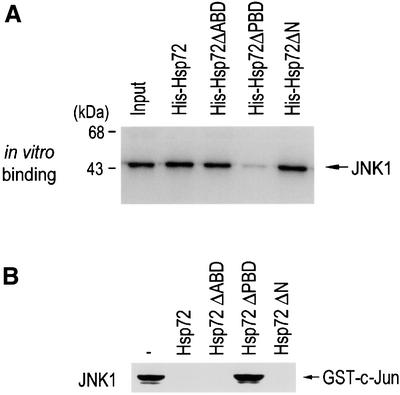
Fig. 6. The peptide binding domain of Hsp72 is critical for the suppression of JNK1 by Hsp72. (A) The peptide binding domain is essential for Hsp72 binding to JNK1 in vitro. In vitro-translated 35S-labeled JNK1 was applied to His-Hsp72 proteins that were bound to Ni2+-NTA–agarose beads. Bead-bound proteins were extensively washed, eluted and analyzed by SDS–PAGE on a 10% polyacrylamide gel and autoradiography. The input 35S-labeled protein (20%) is also shown. (B) The peptide binding domain is essential for Hsp72 to inhibit JNK1. NIH 3T3 cells were exposed to UV (60 J/m2) irradiation, lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-JNK1 antibody. The immunopellets were incubated with 2 µg of wild-type Hsp72 or each mutant protein in 50 µl of HEPES buffer pH 7.4 for 1 h at room temperature, washed twice with HEPES buffer and then assayed for JNK1 activity.
