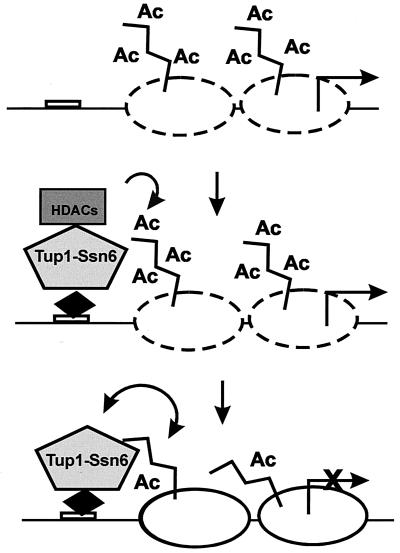
FIG. 9.
Reciprocal interactions between Tup1-Ssn6 and histones. Upon recruitment of Tup1-Ssn6 by sequence-specific repressor proteins (black diamond), associated histone deacetylase (HDAC) activities reduce the acetylation (Ac) of histones in neighboring nucleosomes, facilitating interactions with Tup1. These interactions convert the active chromatin (dashed nucleosomes) to a repressive structure (solid nucleosomes). Moreover, Tup1-histone interactions are self-reinforcing in that they stabilize the association of the corepressor complex with the target promoter and help to maintain the histones in an underacetylated state.