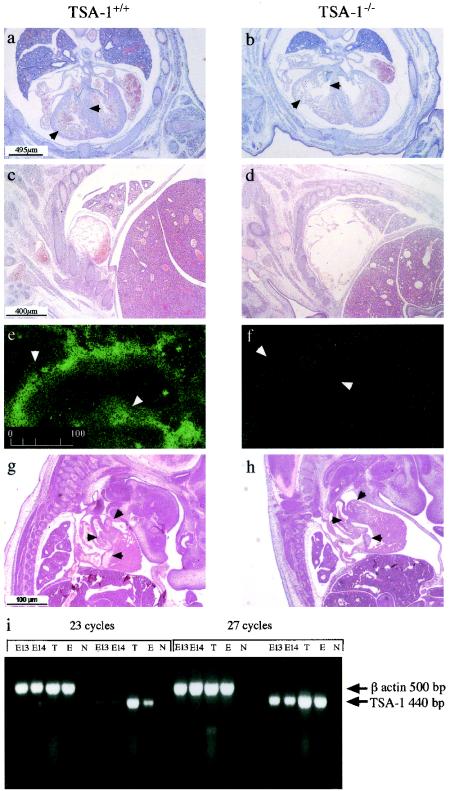
FIG. 4.
Histological anomalies in the developing hearts of TSA-1−/− mice. A comparison of transverse sections from an E14 wild-type fetus (a) and a TSA-1−/− mutant (b). Ventricle walls and interventricular septa are indicated by arrows. Atria of a wild-type E14 (c) and mutant embryo (d). Expression of TSA-1 by immunohistological staining in the aorta (arrowheads) of wild-type E12 (e) and mutant embryo (f). A comparison of sagittal sections of E13 wild-type (g) and mutant embryo (h) showing normal heart valves (arrowheads) in wild-type and mutant embryos. mRNA analysis of TSA-1 expression by RT-PCR in embryonic E13 and E14 hearts (i). Control samples are thymus (T), an olfactory epithelial cell line (E), and no template DNA (N). The TSA-1 oligonucleotide primer target sequences are separated by a 2,000-bp intron (4) and thus would not be expected to amplify TSA-1 genomic sequences.