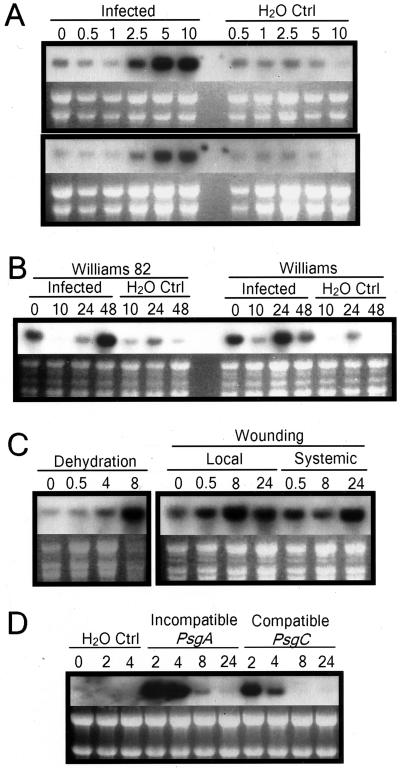
Figure 2.
Northern-blot analyses of the GmMMP2 expression. A, Accumulation of the GmMMP2 transcripts in soybean hypocotyls following infection with the oomycete pathogen P. sojae race 1. The etiolated hypocotyls of 7-d-old seedlings of the resistant cv Williams 82 (top) and susceptible cv Williams (bottom) were inoculated with the zoospores of P. sojae race 1 (infected) or water droplets (H2O Ctrl), and were sampled at the indicated hours after inoculation. B, Accumulation of the GmMMP2 transcripts in soybean leaves following infection with the oomycete pathogen P. sojae race 1. The first trifoliate leaves of 4-week-old plants of the cv Williams 82 and cv Williams were inoculated with the zoospores of P. sojae race 1 (infected) or water droplets (H2O Ctrl), and were sampled at the indicated hours after inoculation. The GmMMP2 activation for the 0-h samples is due to abiotic stresses when the leaves were detached from plants. C, Accumulation of the GmMMP2 transcripts in soybean leaves following dehydration or wounding treatment. At 8 h post-dehydration, the transcription of GmMMP2 reaches the highest level even though the total RNA degraded significantly by that time. The wounding causes a moderate increase in the GmMMP2 transcript accumulation locally and systemically. D, Accumulation of the GmMMP2 transcripts in the suspension-cultured cells of cv Williams 82 following infection with the bacterial pathogen PsgA (incompatible) or PsgC (compatible). The amounts of RNA loaded were visualized by ethidium bromide staining under UV light.