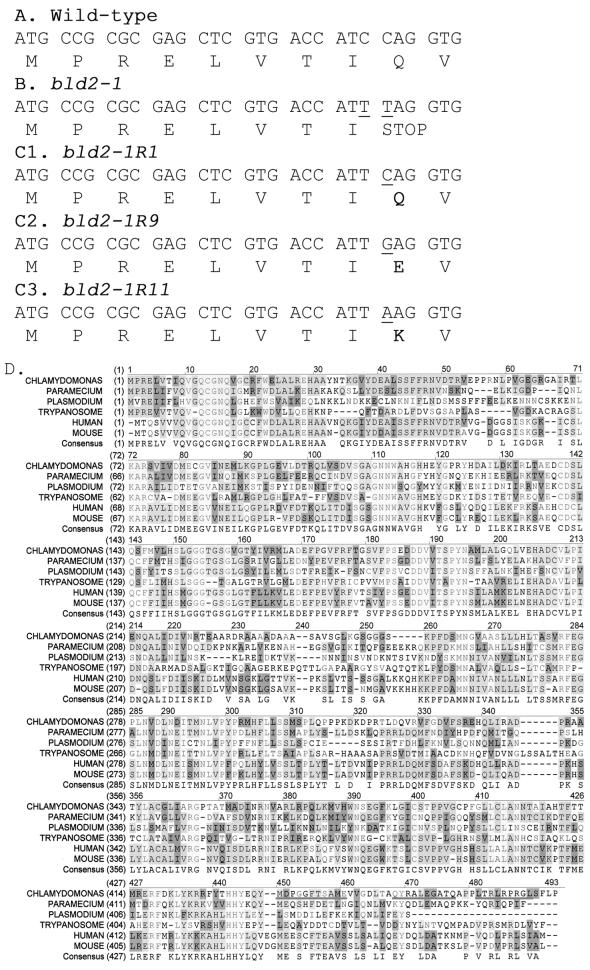
Figure 3.
Nucleotide and amino acids changes in bld2 alleles and alignment of ε-tubulin from multiple organisms. (A) Nucleotide and protein sequence for the first 30 bp of the coding region of ε-tubulin from wild-type cells. (B) From bld2-1 cells, 5743 bp of sequence were obtained. The nucleotide and protein sequences for the first 30 bp of the coding region are shown. There were two C-to-T transition mutations, which are indicated by underlines. (C) Nucleotide and protein sequence for the first 30 bp of the coding region is shown for three intragenic revertant alleles. In each revertant the TAG stop codon is changed to an amino acid. (D) Protein coding sequence of ε-tubulin predicted using Genie trained on 50 Chlamydomonas genes (Kulp et al., 1996) and aligned with ε-tubulin sequences from human, mouse, Trypanosoma, Plasmodium, and Paramecium (see accession numbers in Figure 4). The peptides used for making antibodies are underlined (MDPGGFTSAME, QYRALEGSTQ, and LTRLRPRG). Light gray indicates conservation of the amino acid in all ε-tubulins, medium gray indicates conservation in >50% of the ε-tubulins, dark gray indicates similarity, and white indicates the lack of conservation.