FIG. 3.
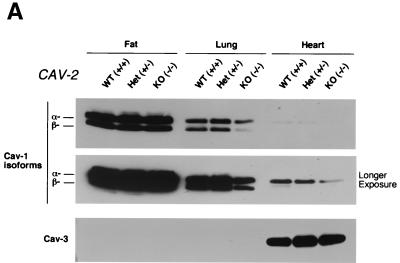
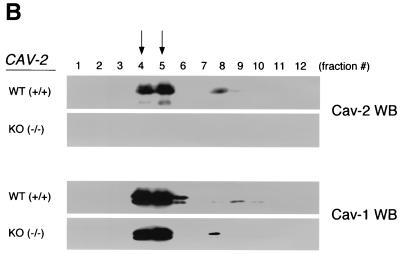
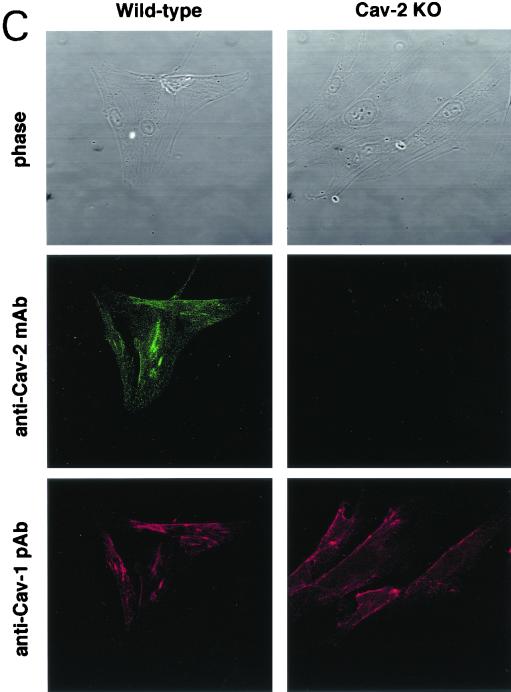
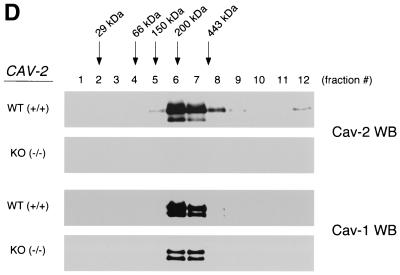
Caveolin-1 expression is mildly reduced but caveolin-1 remains localized to plasma membrane caveolae in Cav-2-null mice. (A) Lysates (30 μg) from the tissues shown in Fig. 1C were loaded in each lane, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with anti-caveolin-1 MAb (clone 2297) and anti-caveolin-3 MAb (clone 65). A longer exposure of the same blot is also shown. Both caveolin-1 and caveolin-3 are expressed in Cav-2-knockout (KO) mice; however, caveolin-1 expression shows a mild reduction in some tissues (≈50% of wild-type levels in lung and heart). Equal protein loading was assessed using the anti-β-tubulin MAb (clone 2.1). (B) Lung tissue from wild-type (WT) and Cav-2-knockout mice was homogenized thoroughly in lysis buffer containing 1% Triton X-100 and subjected to sucrose gradient centrifugation, a procedure that separates caveolar microdomains from other cellular constituents (23). Twelve fractions, of which fractions 4 to 5 and 8 to 12 are considered of caveolar and noncaveolar origin, respectively, were collected and subjected to SDS-PAGE. Immunoblotting with anti-caveolin-2 MAb (clone 26) and anti-caveolin-1 MAb (clone 2297) was used to determine the localization of caveolin-2 and caveolin-1 in these gradient fractions. Arrows point at the caveola-enriched gradient fractions (4 and 5). (C) Formaldehyde-fixed wild-type and Cav-2-knockout MEFs were doubly immunostained with anti-caveolin-1 PAb (N20) and anti-caveolin-2 MAb (clone 26). Bound primary antibodies were visualized with distinctly tagged secondary antibodies (see text). (D) Lung tissue samples from wild-type and Cav-2-knockout mice were homogenized thoroughly in lysis buffer containing 60 mM octylglucoside and subjected to velocity gradient centrifugation, an established procedure that allows the assessment of the size of caveolin oligomers (40, 42, 44, 49). Briefly, solubilized material was loaded atop a 5 to 40% sucrose density gradient and subjected to centrifugation for 10 h. Twelve fractions were recovered, and a 20-μl aliquot from each fraction was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with anti-caveolin-2 MAb (clone 26) and anti-caveolin-1 MAb (clone 2297). Arrows mark the positions of molecular mass standards. Note that caveolin-1 migrates as a high-molecular-mass oligomer of ≈200 to 400 kDa (see fractions 6 and 7) in both wild-type and Cav-2-knockout lung tissue samples. Thus, caveolin-2 expression is not required for the formation of high-molecular-mass caveolin-1 oligomers. Upper panels, caveolin-2 immunoblots; lower panels, caveolin-1 immunoblots.