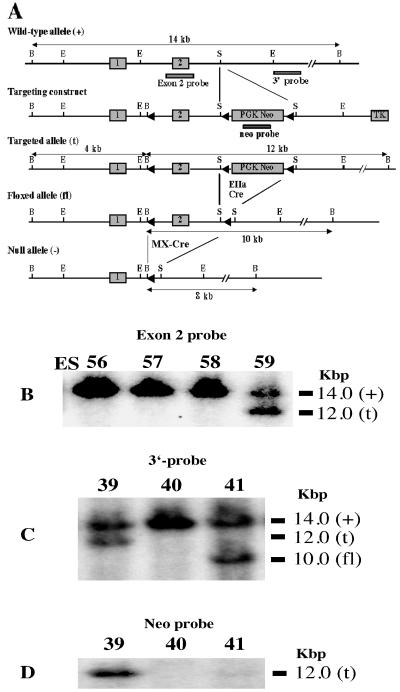
FIG. 1.
Gene targeting and conditional deletion of exon 2 of the PPARγ gene. (A) Restriction maps of the wild-type allele, targeting vector, targeted allele, floxed allele, and null allele. The indicated probes (3′-probe, exon 2, and neo probe) were used to assess recombination events. Open boxes represent exons and are numbered as indicated. PGK neomycin (PGK Neo) and thymidine kinase (TK) are positive and negative selection cassettes, respectively. Restriction sites: B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; S, SacI. (B) Southern blot analysis of homologous recombination in ES cells electroporated with the targeting vector. DNA derived from ES cells were digested with BamHI. Hybridizing fragments of wild-type (+) and targeted (t) alleles to the exon 2 probe and their respective sizes are indicated. Similar results were obtained with the 3′-probe (not shown). (C) Southern blot analysis of BamHI-digested tail DNA from pups derived from the cross between heterozygous (t/+) males and EIIaCre females (schematically shown in panel A). Hybridizing fragments of wild-type (+), targeted (t), and floxed (fl) alleles to the 3′-probe and their respective sizes are indicated. Recombination between loxP sites 2 and 3 was demonstrated with tail DNA derived from the mouse designated “41,” although other recombination events were observed. Similar results were obtained with the exon 2 probe (not shown). (D) Southern blot analysis of tail DNA used in panel C. A 12-kbp hybridizing fragment of the targeted (t) allele, but not wild-type (+) and floxed (fl) alleles, to the neo probe is indicated.