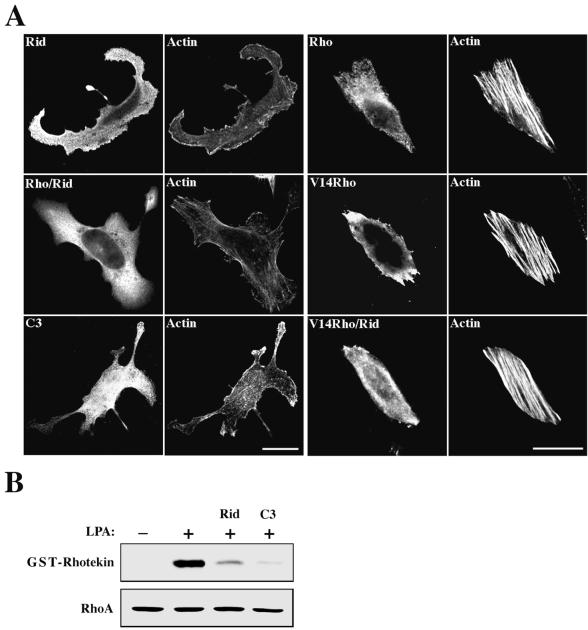
FIG. 3.
Rid inhibits Rho. (A) Rid inhibits Rho-mediated stress fiber formation. HeLa cells grown on coverslips were transiently transfected with an expression vector encoding either HA-Rid (aa 205 to 424), HA-C3 exoenzyme, Myc-tagged wild-type RhoA, or Myc-tagged Val14-Rho or were cotransfected with HA-Rid and Myc-RhoA or with HA-Rid and Myc-Val14-Rho as indicated. Cells were fixed 18 h later and immunostained with either anti-HA (Rid and C3 exoenzyme) or anti-Myc (RhoA and Val14-Rho) or costained with anti-Myc and anti-HA (Rid/Rho and Rid/Val14-Rho) antibodies. Actin morphology was visualized by TRITC-phalloidin staining. Cells coexpressing Rid and Rho were detected by triplet staining with Cy5-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG, Alexa 488-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG, and TRITC-phalloidin. Bars, 10 μm. (B) Rid inhibits LPA-induced RhoA activation. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with expression vectors encoding either Rid or C3 exoenzyme or were mock transfected. The cells were serum starved for 12 h and then stimulated with 10 μM LPA for 5 min. Cell lysates were incubated with GST-rhotekin immobilized on glutathione-agarose beads, and the bound Rho-GTP was analyzed by Western blotting with anti-RhoA antibodies. The level of RhoA expression in each sample was determined by Western analysis using anti-RhoA antibodies (lower panel).