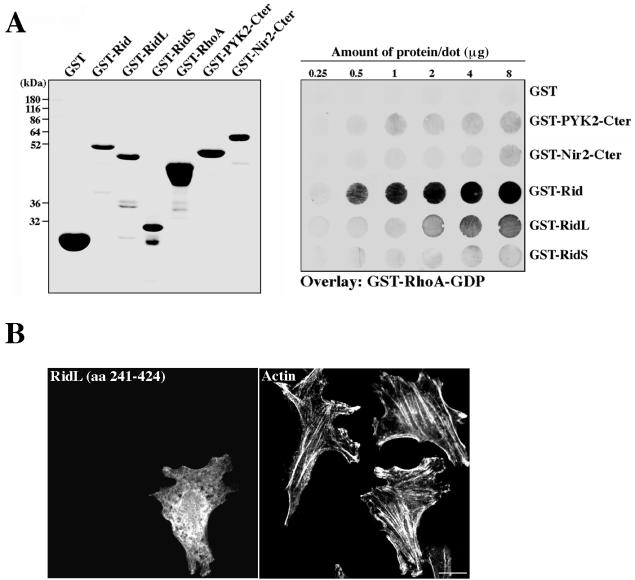
FIG. 7.
Binding of Rho to Rid is critical for Rid's phenotype. (A) Binding of Rho-GDP to Rid and to its truncated mutants. Rid (aa 205 to 424) and its two truncated mutants, RidS (aa 205 to 244) and RidL (aa 241 to 424), were expressed as GST fusion proteins in bacteria and purified on glutathione-agarose beads. Their binding to Rho-GDP was assessed by an overlay assay, essentially as described in the legend to Fig. 6C. The following purified recombinant proteins were used as negative controls: GST, GST fused to the C-terminal region of the tyrosine kinase PYK2 (GST-PYK2-Cter; aa 800 to 1009), and GST fused to the C-terminal region of Nir2 (GST-Nir2-Cter; aa 912 to 1244). Coomassie brilliant blue staining of the purified GST fusion proteins is shown in the left panel. The results of the binding experiment (right panel) indicate that Rid directly and specifically binds Rho-GDP, whereas RidL exhibits weak binding to Rho-GDP, and no detectable binding is observed for RidS. (B) RidL has no effect on actin or cell morphology. Myc-tagged RidL was transiently expressed in HeLa cells, and its effect on the cell and actin morphology was assessed by confocal laser microscopy. As shown, overexpression of this mutant has no obvious effect on either F-actin staining or cell morphology, suggesting that the first 36 aa of Rid are critical for the Rid-induced phenotype. Bar, 10 μm.