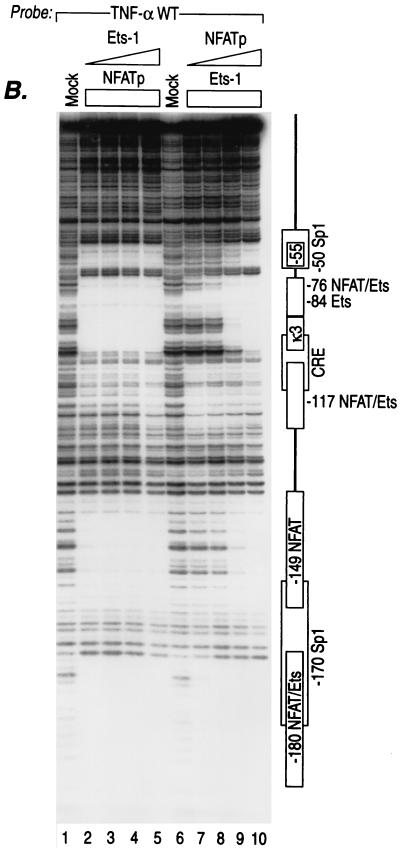
FIG. 4.
Mutually exclusive binding of different activators to shared sites in the TNF-α promoter. (A) Mutually exclusive binding of NFATp and Sp1 to shared sites in the TNF-α promoter. DNase I footprinting results using the wild-type (WT) human TNF-α promoter (nt −200 to +87 relative to the transcription start site) or isogenic probes bearing mutations in the −50 Sp1 site (Sp1 mut or Sp1 cons mut), as described in the text, and increasing concentrations of recombinant NFATp and/or Sp1 are shown. The positions of the six NFAT-binding sites and two Sp1-binding sites are indicated to the left of the panel. (B) Mutually exclusive binding of NFATp and Ets-1 to shared sites in the TNF-α promoter. DNase I footprinting results using the wild-type human TNF-α promoter and increasing concentrations of either recombinant Ets-1 or NFATp are shown. The concentration of recombinant Ets-1 was increased, while NFATp protein was kept at a constant and maximal concentration (lanes 2 to 5), and vice versa: the concentration of recombinant NFATp was increased, while Ets-1 protein was kept at a constant and maximal concentration (lanes 7 to 10). The concentrations of recombinant proteins used are described in detail in the legend to Fig. 1.